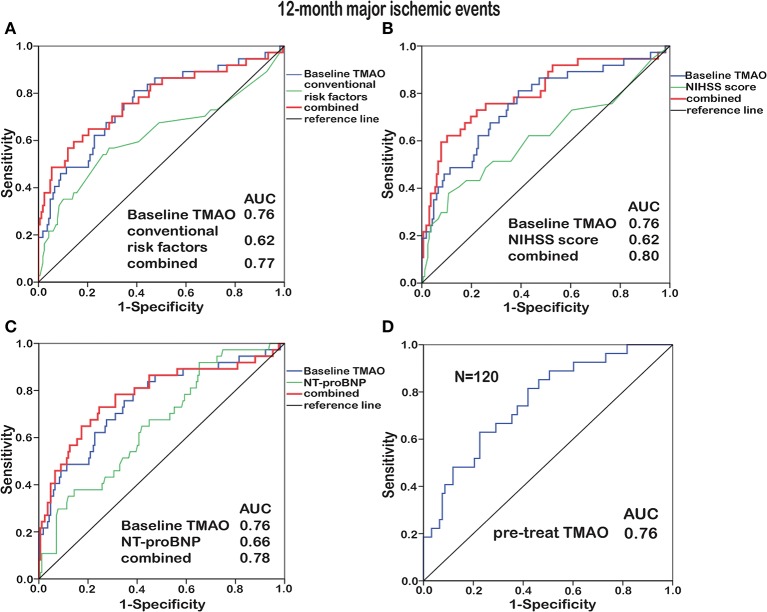
Figure 5.
ROC curve analyses relating baseline TMAO levels and conventional risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, dyslipidemia, and prior stroke; A), the NIHSS scores (B), the NT-proBNP levels (C), as well as the TMAO levels before treatment (pre-treat, N = 120, D), to 12-month major ischemic events. Elevated baseline TMAO levels played a moderate predictive role (AUC = 0.76) in 12-month major ischemic events. Combining baseline TMAO levels with conventional risk factors/the NIHSS scores/the NT-proBNP levels resulted in higher AUCs (p = 0.016, p < 0.001, and p = 0.012, respectively).