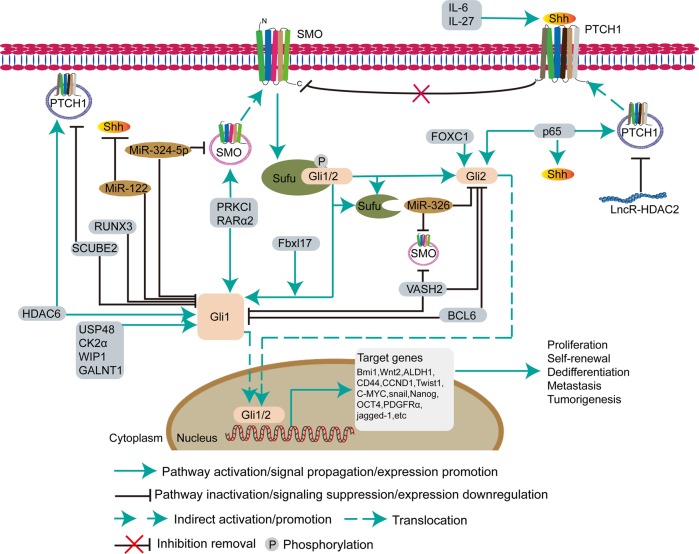
Fig. 2.
Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer stem cells. The Hedgehog pathway plays a key role in stem maintenance, self-renewal, and regeneration of CSCs. The secreted Hh protein acts in a concentration- and time-dependent manner to initiate a series of cell responses, such as cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. After receiving the Shh signal, the transmembrane protein receptor PTCH relieves the inhibition of the transmembrane protein SMO, which induces Gli1/2 to detach from SUFU and enter the nucleus to regulate downstream gene transcription. During activation of the Hh pathway, some proteins (IL-6, IL-27, Fbxl17 (F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 17), PPKCI, RARα2, RUXN3, SCUBE2, HDAC6 (histone deacetylase 6), USP48, CK2α, WIP1, GALNT1, VASH2 (Vasohibin 2), BCL6, FOXC1 (forkhead box C1), and p65), microRNAs (miR-324-5p, miR-122, and miR-326), and the long noncoding RNA HDAC2 are involved in the Hedgehog pathway to affect CSC growth