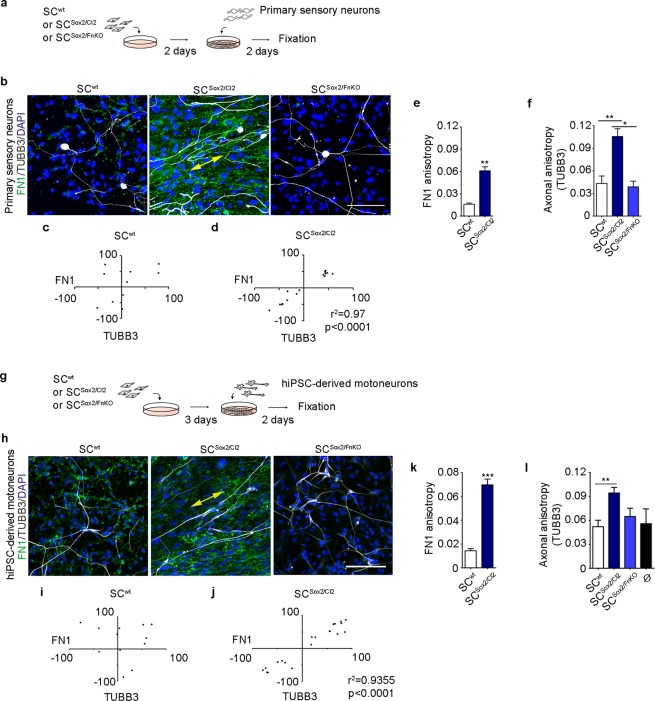
Figure 6.
Neurons align their axons on FN-dependent organized Schwann cells. (a) Experimental design of Schwann cells (SCwt, SCSox2/Cl2 or SCSox2/FnKO) co-cultured with mouse primary sensory neurons. (b) Representative confocal images of FN1 (green) and TUBB3 (white) immunostainings of primary sensory neurons co-cultured with SCwt (129 cells), SCSox2/Cl2 (142 cells) or SCSox2/FnKO (120 cells). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Double head arrow shows the alignment of axons with FN fibres in SCSox2/Cl2. Scale bar, 100 μm. (c,d) Correlation of FN1 fibre angles of SCwt and SCSox2/Cl2 with the axonal angles (TUBB3) (N = 3). (e,f) Quantification of FN1 fibres (N = 3, n ≥ 10 areas) and axonal anisotropy (N = 3, n ≥ 8 areas) in primary sensory neurons co-cultured with: SCwt, SCSox2/Cl2 and SCSox2/FnKO. (g) Experimental design of Schwann cells (SCwt, SCSox2/Cl2 or SCSox2/FnKO) co-cultured with human iPSC-derived motoneurons. (h) Representative confocal images of FN1 (green) and TUBB3 (white) immunostaining of human iPSC-derived motoneurons co-cultured with SCwt (211 cells), SCSox2/Cl2 (231 cells) or SCSox2/FnKO (245 cells). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Double-head arrow shows the alignment of axons with FN fibres in SCSox2/Cl2. Scale bar, 100 μm. (i,j) Correlation of FN1 fibre angles of SCwt and SCSox2/Cl2 with the angles of human iPSC-derived motoneurons (TUBB3) (N = 3). (k,l) Quantification of FN1 fibres (N = 3, n ≥ 18 areas) and axonal anisotropy (N = 3, n ≥ 9 areas) of human iPSC-derived motoneurons co-cultured with: SCwt, SCSox2/Cl2 and SCSox2/FnKO. Ø corresponds to human iPSC-derived motoneurons cultured alone. Results are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005.