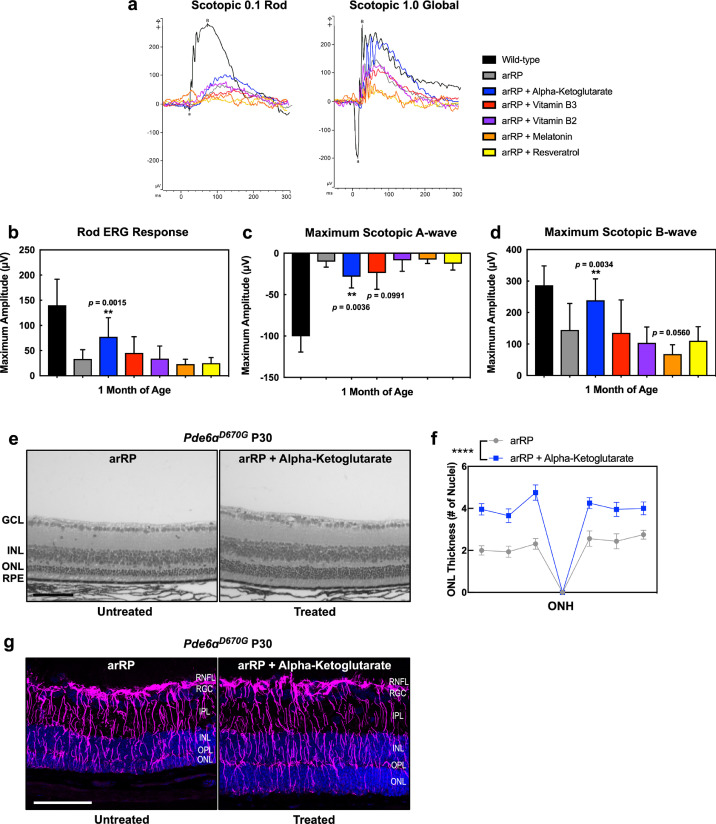
Fig. 7.
Oral supplementation of single metabolites rescues photoreceptor cell survival and visual function in the arRP preclinical mouse. (a) Representative traces of the scotopic 0.1 (flash strength in cd·s·m−2) dim-light rod-specific electroretinography (ERG; left) and scotopic 1.0 (flash strength in cd·s·m−2) global ERG (right) in Pde6ɑD670G mice treated with ɑ-KG (blue), vitamin B2 (purple), vitamin B3 (red), melatonin (orange) or resveratrol (yellow) supplementation in comparison to untreated Pde6ɑD670G mice (gray) and wild-type controls (black) at one month of age. Quantification of ERGs from a cohort of mice treated with ɑ-KG (blue), vitamin B2 (purple), vitamin B3 (red), melatonin (orange) or resveratrol (yellow) supplementation shows significant visual rescue of (b) the rod photoreceptor cell response, (c) the maximum scotopic a-wave response, and (d) the maximum scotopic b-wave response in mice treated with ɑ-KG supplementation (blue) in comparison with wild-type controls (black) or untreated Pde6ɑD670G mice (gray) at one month of age. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 [1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison's test]. N = 5 WT, 6 arRP, 11 arRP + ɑ-KG mice, 8 arRP + vitamin B3, 7 arRP + vitamin B2, 8 arRP + melatonin and 7 arRP + resveratrol. (e-f) Histological analysis of the retinas of untreated Pde6ɑD670G mice (left) compared to treated Pde6ɑD670G mice (right) shows a significant increase in the thickness of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) by number of photoreceptor cell nuclei in mice treated with ɑ-KG supplementation (blue) at one month of age. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bar = 100 µm. (f) Results are displayed as a morphometric quantification (spider graph) of ONL layer thickness superior (left) and inferior (right) to the optic nerve head (ONH). Wild-type mice have an ONL thickness of approximately 10 nuclei. ****p < 0.0001 [Student's t-test]. N = 3 wild-type and 4 arRP + ɑ-KG eyes, with multiple ONL thickness counts per eye as described in Methods. Error bars = SEM. (g) Extensive Müller glial cell activation seen in arRP mice with and without ɑ-KG treatment. Retinas were dissected at one month of age from untreated arRP mice and arRP mice treated with ɑ-KG beginning at postnatal day 0. Retinas were stained with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; purple) and DAPI (blue) to identify retinal nuclei. In both the untreated arRP (left) and ɑ-KG treated (right) arRP mice there is increased expression of GFAP in Müller glia spanning the retina, suggesting that the treatment has no effect on Muller glial activation. N = 3 per group. Images taken at 25× magnification. Scale bar = 100 μm.