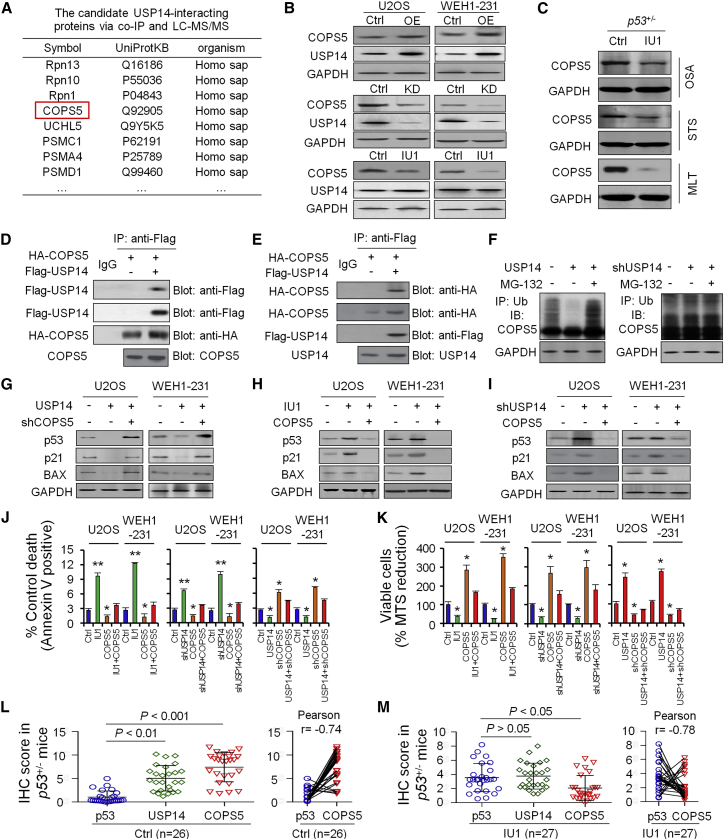
Figure 4.
IU1 Inhibits USP14 Deubiquitinating Activity to Upregulate p53 through COPS5
(A) Coimmunoprecipitation (coIP) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used to screen the candidate of USP14-interacting proteins. (B) Western blotting was used to quantify COPS5 protein level in U2OS and WEH1-231 cells after IU1 treatment, USP14 knockdown, or overexpression. (C) Western blotting was used to quantify COPS5 protein level in OSA, STS, and MLT tissues from p53+/− mice. (D and E) Immunoprecipitation analysis by either anti-HA (D) or anti-Flag antibody (E) after HA-COPS5, together with Flag-USP14 expression plasmid, was cotransfected in 293T cells. (F) COPS5 ubiquitination level was detected in vitro in 293T cells after USP14 overexpression or treatment with MG-132. (G–I) p53, p21, and BAX protein level was detected in vitro in U2OS and WEH1-231 cells after USP14 overexpression and COPS5 knockdown (G), COPS5 knockdown with IU1 treatment (H), or USP14 knockdown and COPS5 overexpression (I). (J) Bar graphs (mean ± SD) show percentage of AnxV+ cells treated with DMSO (Ctrl), IU1 treatment, knockdown, and overexpression of USP14 or COPS5. (K) Viability was measured in U2OS and WEH1-231 cells treated with DMSO (Ctrl), IU1 treatment, knockdown, and overexpression of USP14 or COPS5. (L and M) Expression and association of p53, USP14, and COPS5 in primary tumor tissues from p53+/− mice treated with DMSO (L; Ctrl, n = 26) or IU1 (M; n = 27).