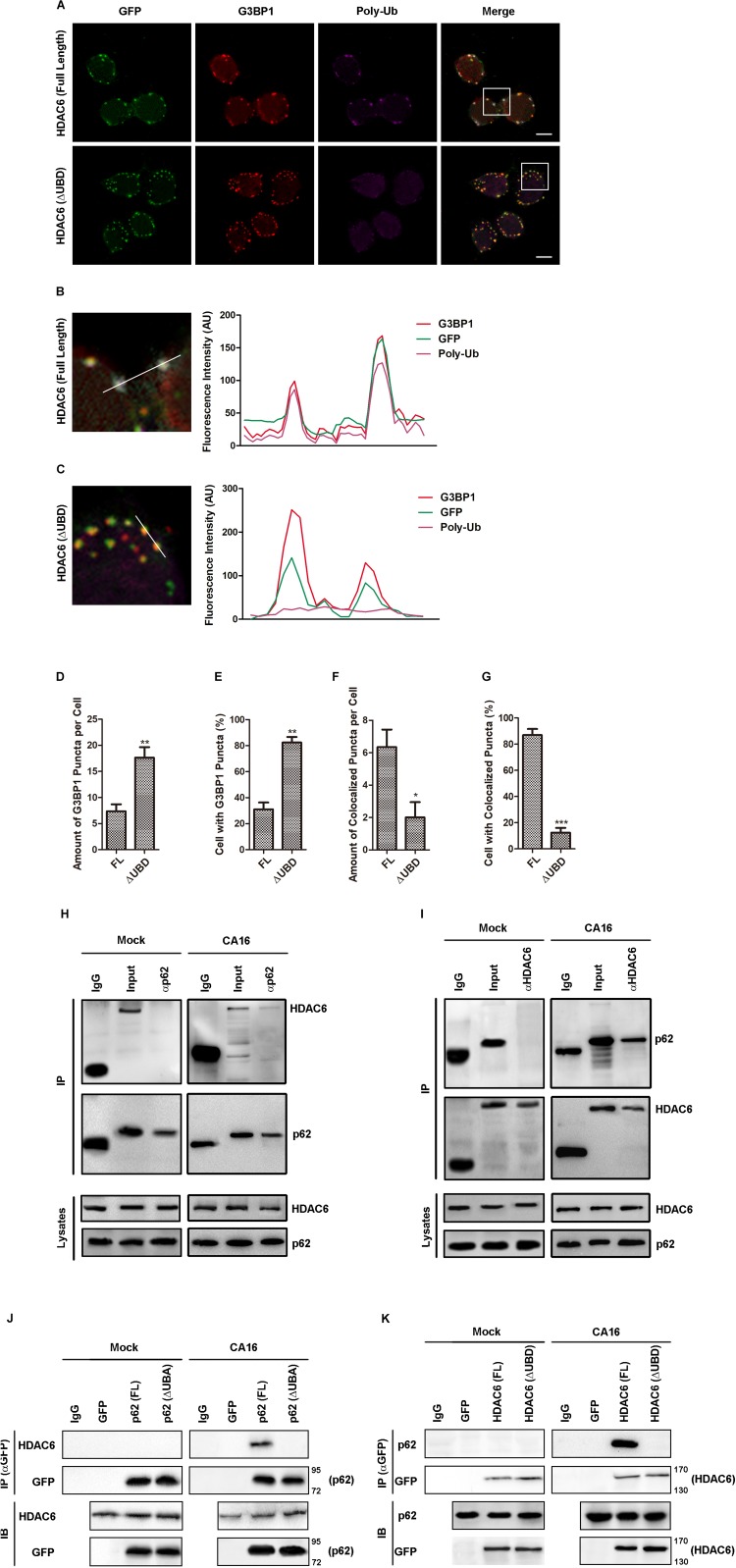
FIGURE 6.
The UB domain of HDAC6 was critical for p62-mediated autophagic clearance of SGs in CA16-infected cells. (A) RD cells expressing GFP-HDAC6 [HDAC6 (full length)] or GFP-HDAC6 with ubiquitin binding domain deletion [HDAC6 (ΔUBD, Δ1154aa-1189aa)] were subjected to CA16 infection at an MOI of 1 for 24 h. The intracellular distribution of G3BP1 and GFP was examined by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 5 μm. (B) and (C) The white box (inset) shows the zoomed image. The fluorescence intensity of G3BP1, GFP, and poly-Ub along the indicated line were scanned. (D–G) Quantitation of the data in (F). Graphs show the mean ± SEM, 6 random fields and 10 cells per field were examined for confocal microscopy. (H) and (I) RD cells were infected with CA16 at an MOI of 1 for 4 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with (H) anti-p62 or (I) anti-HDAC6 antibody. Immune complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-HDAC6 and anti-p62 antibodies. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (J) RD cells expressing GFP-p62 [p62 (full length)] or GFP-p62 with ubiquitin-associated domain deletion [p62 (ΔUBA, Δ404aa-425aa)] were subjected to CA16 infection at an MOI of 1 for 4 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody. Immune complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-HDAC6 and anti-GFP antibodies. (K) RD cells expressing GFP-HDAC6 [HDAC6 (full length)] or GFP-HDAC6 with ubiquitin-binding domain deletion [HDAC6 (ΔUBD, Δ1154aa-1189aa)] were subjected to CA16 infection at an MOI of 1 for 4 h. Immune complexes were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-p62 and anti-GFP antibodies. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.