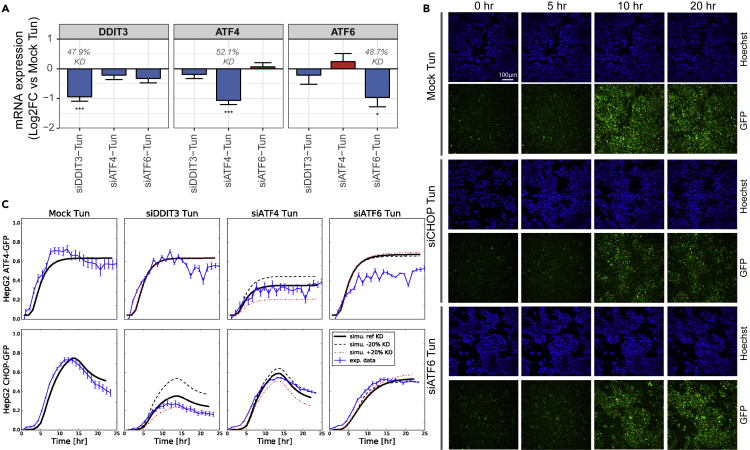
Figure 5.
Perturbation of UPR with siRNA Knockdowns Are Consistent with Model Predictions
(A) Log2 fold changes of mRNA expression of different siRNA-mediated gene knockdowns relative to siRNA mock negative control in HepG2 WT cells exposed to 6 μM of tunicamycin for 16 h, determined using TempO-seq transcriptomics. Knockdown efficiencies of siRNAs are depicted in gray numbers. Data represent the mean ± SE of three biological replicates.
(B) Representative confocal microscopy images obtained with 20× objective of HepG2 CHOP-GFP reporter cells exposed to 6 μM of tunicamycin for 16 h after CHOP, ATF6, or Mock siRNA. To visualize the nuclei, cells were stained with Hoechst (upper rows), and CHOP-GFP is represented in green (lower rows).
(C) Model simulation of ATF4 and CHOP (black curves) compared with quantified GFP data after exposure to 6 μM of tunicamycin for different siRNA-mediated knockdown conditions (blue line and error bars representing mean ± SE of three biological replicates). Simulations with varied knockdown efficiency (black dashed: 20% less, red dashed: 20% more) are also plotted.