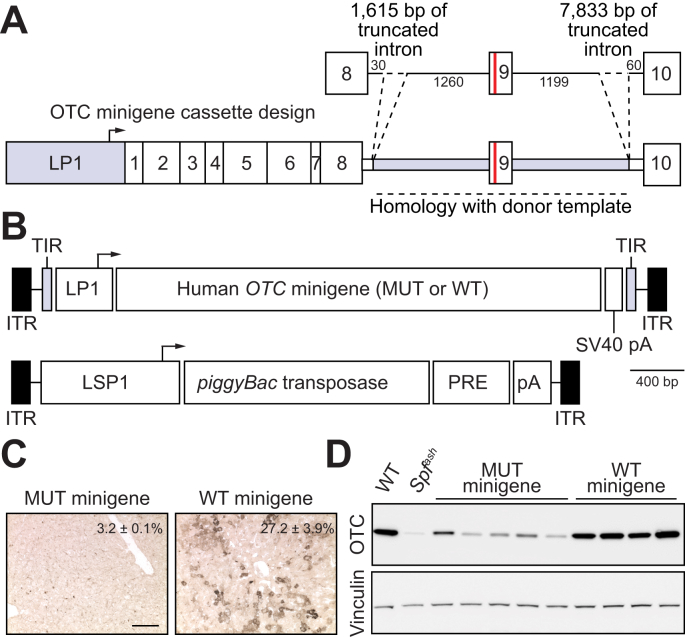
Fig. 1.
Functional analysis of human minigenes.
(A) Schematic representation of the human OTC minigene containing a point mutation in exon 9 (c.905A>T; p.H302L; red line) that causes severe OTC deficiency with neonatal presentation. Minigene expression is driven by a liver-specific promoter/enhancer (LP1) comprising an ApoE enhancer and short form of the hAAT promoter.47 Intronic sequences flanking exon 9 are shaded in grey. (B) Configuration of the hybrid AAV/piggyBac transposase system used in the study with the structure of the cloned minigene indicated in panel (A) above. ITRs are indicated by the black rectangular boxes and the piggyBac transposase is expressed from the LSP1 promoter containing two copies of the ApoE enhancer and long form of the hAAT promoter. Minigenes were delivered to newborn Spfash mice by intraperitoneal injection using the hybrid AAV/piggyBac transposase vector system. Animals received 1.5×1010 vg transposase and 1×1011 vg minigene vectors (both packaged in the AAV8 capsid) and were harvested 4 weeks later (n = 5 for the mutant and n = 4 for the WT minigenes, respectively). OTC activity (percent WT, mean ± SEM) and expression levels were determined in (C) liver sections (scale bar = 50 μm) and (D) by Western blot analysis. Lysates from WT and Spfash mice were included as controls.
AAV, adeno-associated virus; ApoE, apolipoprotein E; hAAT, human alpha 1-antitrypsin; ITRs, inverted terminal repeats; LP1 and LSP1, liver-specific promoters;7 pA, bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal sequence; PRE, mutant form of the Woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element; SV40 pA, SV40 polyadenylation signal sequence; WT, wild-type.