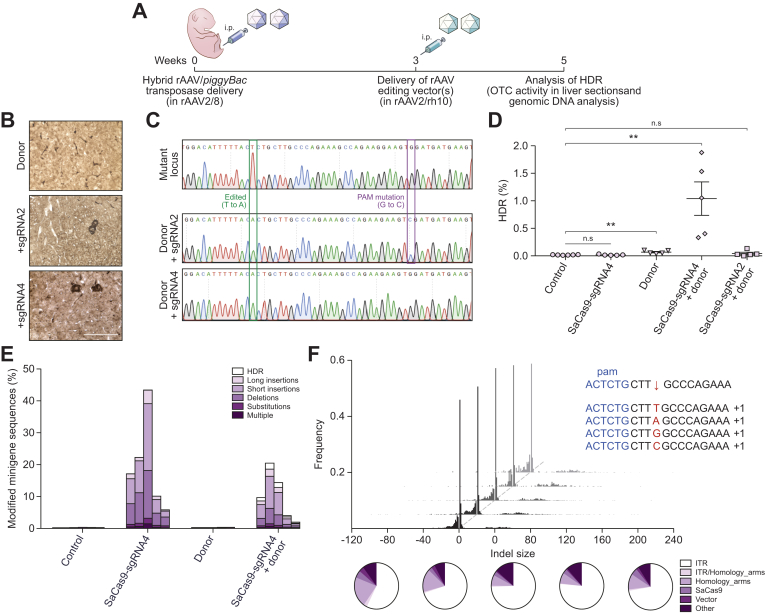
Fig. 3.
Homology-directed repair of the transposed human OTC locus in Spfashmice.
(A) Experimental overview and timing of intraperitoneal rAAV delivery for CRISPR-SaCas9-mediated HDR in Spfash mice. Newborn animals received 5×1010 vg transposase and 1×1011 vg mutant minigene vectors (packaged in rAAV2/8 capsid) and 3 weeks later, 2×1011 SaCas9/sgRNA and/or 5×1011 donor vectors (packaged in rAAV2/rh10 capsid). Mutant minigenes were delivered (intraperitoneal) to newborn spfash mice using the hybrid AAV/piggyBac transposase vector system and 3 weeks later animals received genome editing vectors; n = 5 per treatment group. HDR was confirmed 2 weeks later by (B) the presence of functional OTC activity in liver sections (scale bar = 50 μm) and (C) by Sanger sequencing analysis of cloned OTC amplicons amplified using primers with binding sites outside the region of homology with the donor vector. Next-generation Illumina® sequencing was performed across the transposed OTC human minigene locus to more accurately (D) quantitate the HDR rates and (E) characterise the unintended modifications found at the SaCas9 cleavage site. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. and significance evaluated using the Mann-Whitney non-parametric test (**p <0.005). Control samples represent PCR amplicons amplified from Spfash mice that did not receive genome editing vectors following minigene delivery. (F) In addition to the expected InDels, with a 1 bp insertion the most commonly detected event (insert, top right), large insertions (>10 bp) were observed at the cleavage site. Notably, insertions containing ITR sequences were over-represented (indicated by the white region of the pie diagrams). Each histogram and pie diagram represent an individual animal that received 2×1011 vg SaCas9-sgRNA4 and 5×1011 vg donor vectors. AAV, adeno-associated virus; HDR, homology-directed repair; InDels, insertions and deletions; ITR, inverted terminal repeat; SaCas9, Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 nuclease; sgRNA, single guide RNA; rAAV, recombinant AAV.