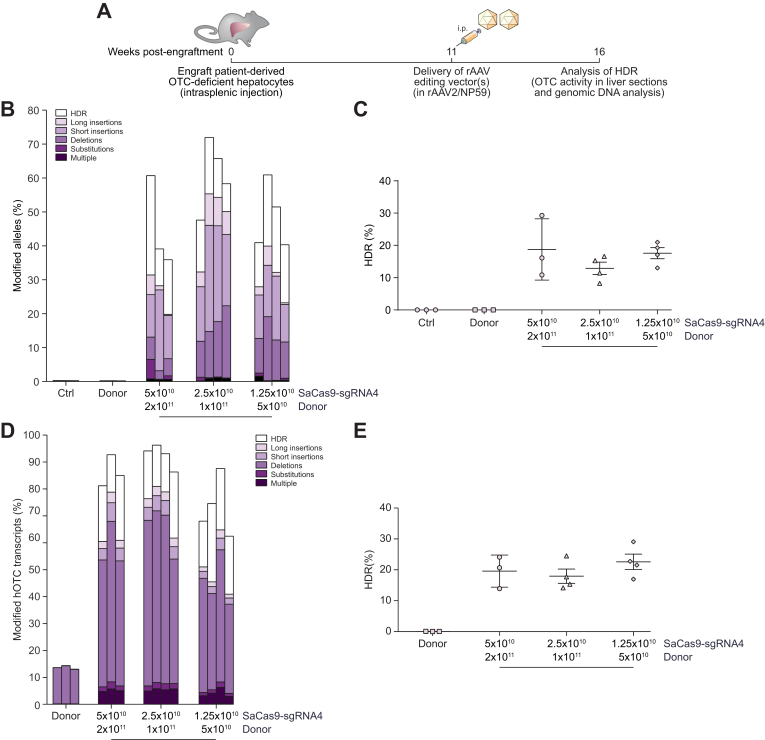
Fig. 4.
Efficient correction of OTC-deficient patient-derived primary human hepatocytes in vivo.
(A) Experimental overview. Cells were engrafted into FRG mice and repopulation established by cycling on and off the drug 2-(2-nitro-4-fluoromethylbenzoyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedione.20 Eleven weeks later, when the mice were on day 11 of a 21-day water cycle, animals received 5×1010 vg/mouse SaCas9-sgRNA4 and 2×1011 vg/mouse donor vectors, 2.5×1010 vg/mouse SaCas9-sgRNA4 and 1×1011 vg/mouse donor vectors or 1.25×1010 vg/mouse SaCas9-sgRNA4 and 5×1010 vg/mouse donor vectors packaged in the NP59 capsid via intraperitoneal delivery (n = 3 per treatment group for controls and highest vector dose, and n = 4 for 2 lower vector doses). Livers were analyzed 5 weeks following vector delivery. Next-generation Illumina® sequencing was performed across the OTC locus from (B, C) genomic DNA and (D, E) cDNA isolated from FRG mice transplanted with patient-derived human hepatocytes to quantitate the HDR rates and characterise the unintended modifications found at the SaCas9 cleavage site. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. Control samples represent PCR amplicons from engrafted FRG mice that did not receive AAV vector treatment. AAV, adeno-associated virus; FRG, Fah-/-Rag2-/-Il2rg-/; HDR, homology-directed repair; InDels, insertions and deletions; ITR, inverted terminal repeat; SaCas9, Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 nuclease; sgRNA, single guide RNA; rAAV, recombinant AAV.