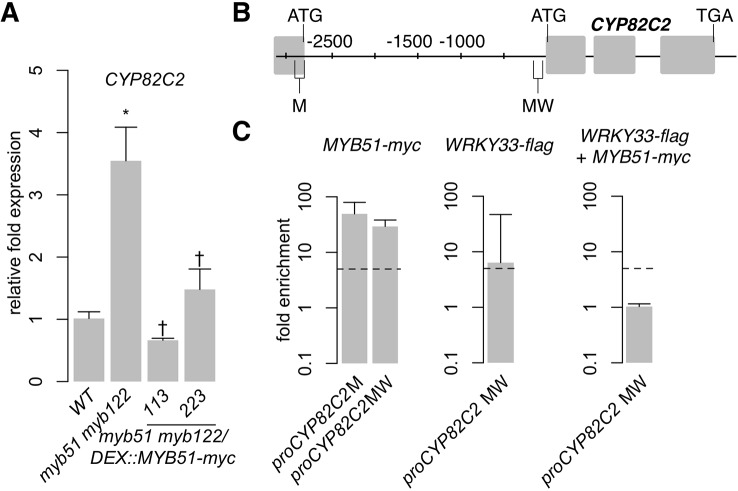
Figure 6.
MYB51 directly represses SMRE-containing CYP82C2 promoter. (A) qPCR analysis of CYP82C2 in 9-day-old seedlings co-elicited with 20 μM Dex and Psta for 12 h. Data represent the mean ± SE of four replicates of 13–17 seedlings each. Expression values were normalized to that of the housekeeping gene EIF4A1 and relative to those of WT plants. Asterisks and daggers denote statistically significant differences compared to wild-type and myb51 myb122, respectively (P < 0.05, two-tailed t test). (B, C) Nucleotide positions (B), ChIP-PCR analysis (C, left and middle), and sequential ChIP-PCR analysis (C, right) of SMRE (M), W-box (W), and SMRE and W-box (MW)–containing CYP82C2 promoter regions bound by MYB51-myc and/or WRKY33-flag in 9-day-old seedlings co-elicited with 20 μM Dex or mock solution (0.5% DMSO) and Psta for 9 h. Dashed lines represent the fivefold cutoff between weak and strong TF–DNA interactions. Data in (C) represent the median ± SE of three (right) and four (left and middle) biological replicates, each containing approximately 200 seedlings. Experiments in (A, C) were performed twice, producing similar results.