Figure 7. Model for synthetic lethal interaction between VPS4A and VPS4B .
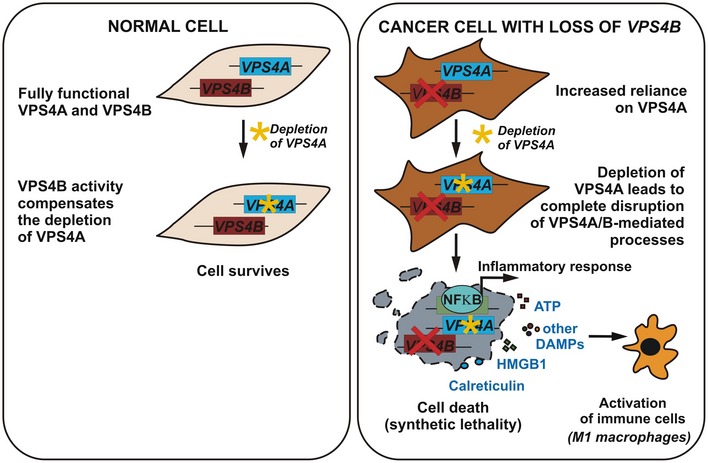
Left panel, in normal cells, both VPS4A and VPS4B act redundantly in several essential intracellular processes. So, a single depletion of any VPS4 paralog (e.g., VPS4A) is tolerated, as unperturbed expression of the other paralog alone (e.g., VPS4B) suffices to substitute for its downregulated counterpart. Right panel, cells that have lost VPS4B expression, e.g., due to oncogenic genome rearrangements, rely exclusively on VPS4A activity. So, inactivation of VPS4A in these cells leads to synthetic lethality that is accompanied by strong induction of an inflammatory response and release of immunogenic DAMPs. Immunomodulatory molecules released by dying VPS4A+B‐deficient cancer cells can elicit paracrine effects on primary immune cells, e.g., reprogramming of macrophages toward the M1 anti‐tumor phenotype.
