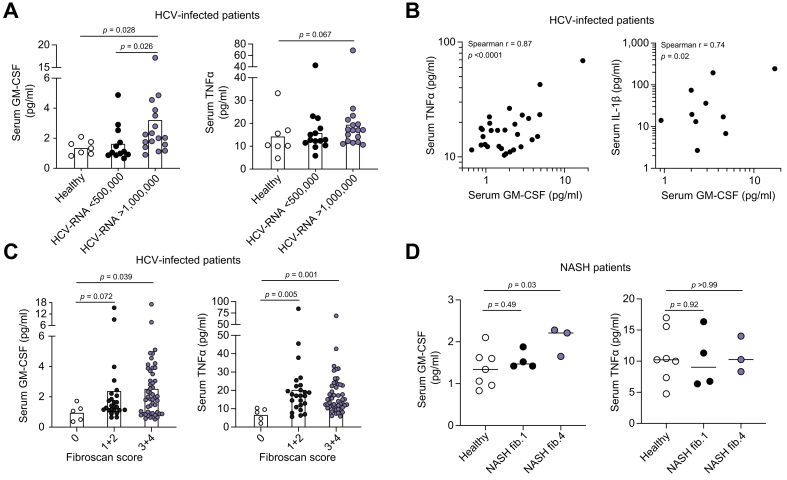
Fig. 2.
Elevated serum GM-CSF concentrations are associated with advanced liver fibrosis and systemic inflammation in patients with viral-related liver disease.
Serum GM-CSF (left panel) and TNFα (right panel) concentrations were measured by Luminex in (A) healthy human donors (n = 7) or CHC patients before DAA therapy with low (<5×105IU/ml, n = 12) or high (>1×106IU/ml, n = 17) viremia. Values are shown as mean concentration (pg/ml). (B) Correlative analyses of serum GM-CSF, TNFα and IL-1β concentrations from all CHC patients (high and low viremia) by Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. (C) Serum GM-CSF (left panel) and TNFα (right panel) concentrations were measured in all CHC patients (before and after DAA therapy) with a Fibroscan score of 0 (n = 5), 1-2 (n = 25) and 3-4 (n = 46 for GM-CSF, 4 out of range, and n = 50 for TNFα). (D) Serum GM-CSF (left panel) and TNFα (right panel) concentrations were measured in healthy controls (n = 7) and patients with NASH and a fibrosis score of 1 (n = 4) or of 4 (n = 3). p values calculated by Mann-Whitney test or Spearman's correlation. CHC, chronic hepatitis C; DAA, direct-acting antiviral; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.