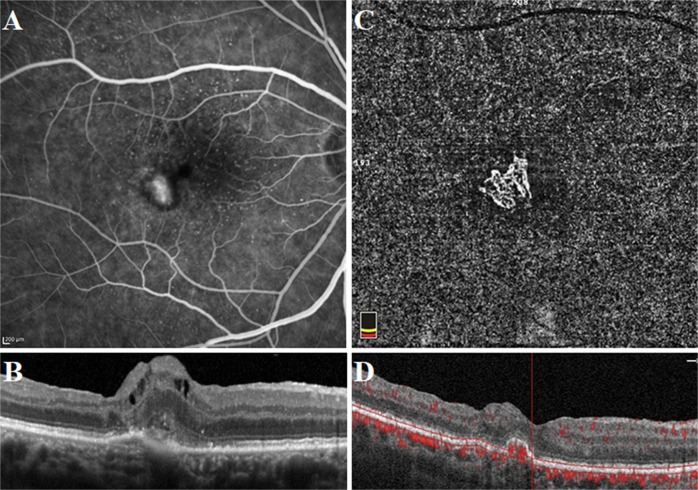
Fig. 4.
Well-defined neovascular complex in a 69-year-old female patient who had a history of active mixed-type neovascularization treated with eight anti-VEGF injections 2 years before the optical coherence tomography angiography acquisition. At the presentation, fluorescein angiography image demonstrated a hyperfluorescent area representing the neovascular complex (a). Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography horizontal line scan indicated the neovascular complex both above and beneath the retinal pigment epithelium (b). At the time of study evaluation, the neovascular complex with vessels radiating from one side of the lesion (sea-fan) was demonstrated on the optical coherence tomography angiography en face projection image (c). Cross-sectional optical coherence tomography angiography revealed abnormal flow signal beneath the retinal pigment epithelium in the choroid slabs (d)