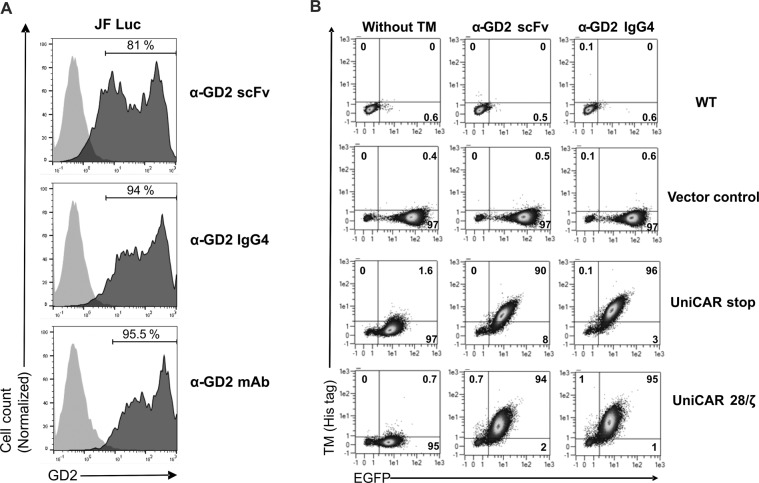
Figure 5.
Binding of scFv- and IgG4-based α-GD2 TMs to neuroblastoma cells and UniCAR NK-92 cells. (A) JF Luc neuroblastoma cells were incubated with α-GD2 scFv or α-GD2 IgG4 TMs. TM binding to the surface of the cells was then detected with antibody 5B9 specific for the E5B9 epitope tag, followed by Alexa Flour 647-conjugated goat α-mouse antibody (dark grey areas). Control cells were incubated with antibody 5B9 and secondary antibodies in the absence of a TM (light grey areas). In addition, cells were either stained with α-GD2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) or isotype control (bottom panel; dark and light grey areas, respectively). (B) To detect binding of the TMs to UniCAR-expressing NK-92 cells, 1.5 × 105 UniCAR 28/ζ and UniCAR stop NK-92 cells were incubated with α-GD2 scFv or α-GD2 IgG4 TMs. TM binding was detected using a PE-conjugated polyhistidine-specific antibody. Parental NK-92 cells (WT) and NK-92 cells transduced with EGFP-encoding vector (Vector control) were included as controls. Numbers shown in the density plots indicate the percentage (%) of positive cells in each gate.