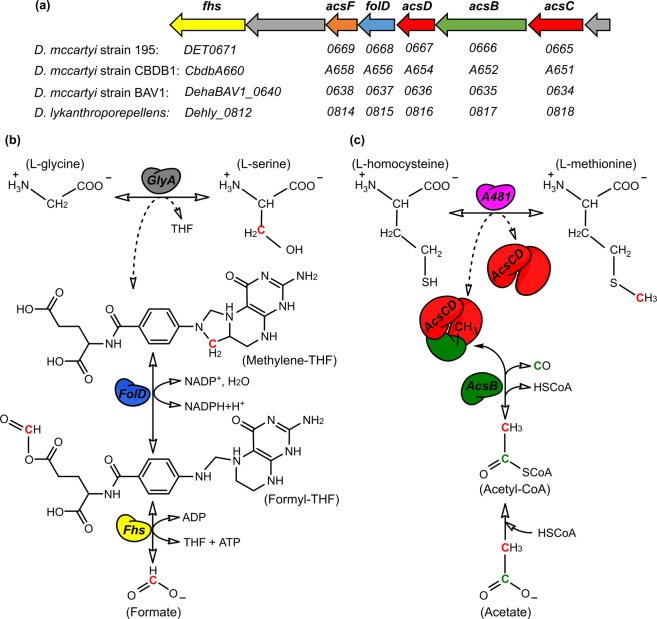
Figure 6.
Pathways of L-glycine and L-homocysteine methylation in Dehalococcoides species and hypothesized involvement of THF and corrinoid proteins. (a) Genes annotated to be involved in the incomplete Wood-Ljungdahl pathway encoded in D. mccartyi strain 195 and the respective homologous genes in other Dehalococcoidia. (b) L-serine formation via glycine hydroxymethyltransferase (GlyA, grey) as proposed by Zhuang et al. is shown32. The methyl group is derived most probably from formate with the aid of formyl-tetrahydrofolate synthase (Fhs, yellow) and methylene-tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase (FolD, blue). (c) Methylation of L-homocysteine is conducted by core-MetECBDB encoded by the locus cbdbA481 (purple) in D. mccartyi strain CBDB1. The original source of the methyl group is acetate, which is activated to acetyl-CoA and then cleaved by acetyl-CoA decarbonylase (AcsB, green) into HSCoA, carbon monoxide (CO) and a methyl group. The standard activity of AcsB is to transfer the methyl group to a corrinoid iron-sulfur protein complex (CoFeSP) AcsCD (red). We speculate that the methyl group is directly transferred from the CoFeSP to the core-MetECBDB (A481) for L-homocysteine methylation (dashed arrow) but this transfer could also be indirect via a yet unidentified participant.