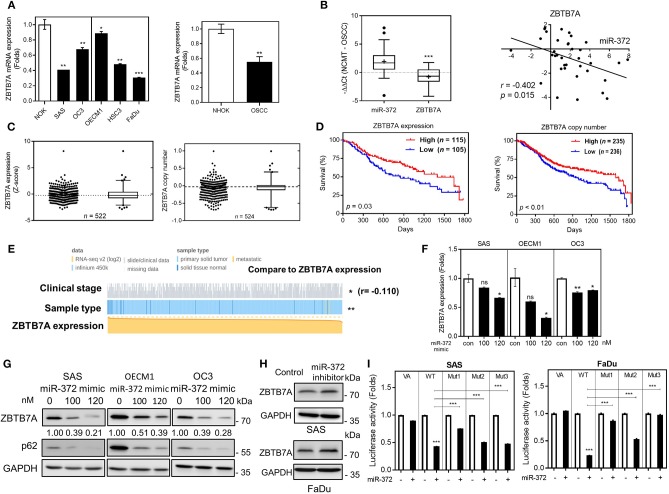
Figure 1.
ZBTB7A downregulation in OSCC is due to miR-372 targeting. (A) ZBTB7A mRNA expression in OSCC cell lines and normal oral keratinocytes (NOK). Lt panel, individual comparison. Vertical line separates cells having wild-type p53 (Lt) and mutant p53 (Rt). Rt panel, overall comparison. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of OSCC tissue pairs. Lt, upregulation of miR-372 expression and downregulation of ZBTB7A mRNA expression in OSCC tumors. Rt, correlation analysis showing a reverse correlation between miR-372 expression (X-axis) and the ZBTB7A mRNA expression (Y-axis) in tumors. (C–E) Analysis of the TCGA HNSCC database. (C) Lt, ZBTB7A expression. Rt, ZBTB7A copy number. In each figure panel, both dot plot (Lt) and Box-and-Whiskers plot (Rt) are shown. Median values marked by dot-lines and are used as cut-offs in order to define high vs. low. (D) Kaplan-Meier analysis of patient overall survival according to ZBTB7A expression (Lt) and ZBTB7A copy number (Rt). (E) Association between ZBTB7A expression and clinicopathological parameters. ZBTB7A expression is significantly associated with sample origin (normal tissue vs. tumor tissue) and stages. r in (B,E), correlation coefficient. (F,G) miR-372 expression downregulates ZBTB7A mRNA expression (in F) and protein expression (in G) in a dose-dependent manner. (H) miR-372 inhibition slightly upregulates ZBTB7A expression in SAS (Upper) and FaDu (Lower) cells. (I) Luciferase reporter assay showing the direct targeting of miR-372 onto the 3'UTR of ZBTB7A (VA, vector alone; WT, wild-type reporter; Mut1–Mut3, mutant reporters). The potential target sequences within the wild-type reporter are replaced by restriction enzyme sites in the three mutant reporters. ns, not significant, *p <0.05; **p <0.01; ***p <0.001.