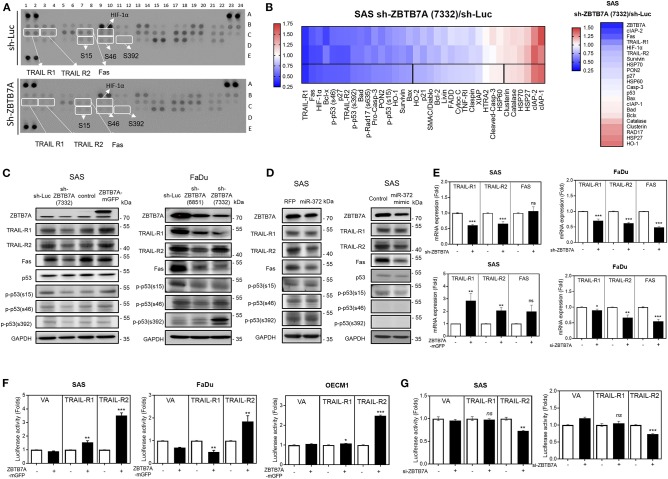
Figure 4.
ZBTB7A expression is associated with the expression of death receptors and the phosphorylated isoforms of p53 in OSCC cells. (A,B,D) SAS cells. (A) Apoptosis array. A panel of 35 antibodies including various forms of phosphorylated p53 were measured in duplicate using this array. The ZBTB7A knockdown cell subclone and the control cells were treated with CDDP for 24 h, and then the array was used to identify changes in various apoptosis factors. Lt, a diagram of the array. White rectangles indicate duplicates exhibiting significant changes in signal following ZBTB7A knockdown. Rt, a heat-map demonstrating the changes in protein profile following ZBTB7A knockdown. The 3rd lane represents the average value of the duplicate signals in the upper two lanes. Vertical lines define the 20 proteins that are downregulated >30% (Lt region) or that are upregulated >12% (Rt region). (B) RNA sequencing. A heat-map showing the changes in transcript levels in the ZBTB7A subclone. The genes selected for analysis are TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, Fas and the various phosphorylated isoforms of p53 and many of these were downregulated following knockdown of ZBTB7A; thus these are to be considered as ZBTB7A targets during apoptosis modulation. (C,D) Western blot analysis. (C) Lt, SAS cells, Rt, FaDu cells. Expression of TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, Fas, and p53 phosphorylated at serine 15 is correlated with ZBTB7A expression (in C), and is inversely correlated with ZBTB7A knockdown (in C) and miR-372 expression (in D) in OSCC cells. (E) qRT-PCR analysis. This shows the concordant changes in TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 mRNA expression in OSCC cells following ZBTB7A knockdown/expression. (F,G) Promoter activity assay. This shows the consistent increase and decrease in TRAIL-R2 activity that follows expression and transient knockdown of ZBTB7A in OSCC cells, respectively. ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.