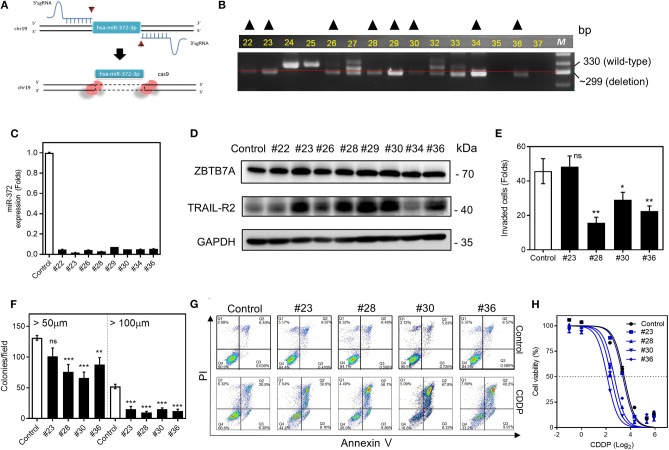
Figure 6.
miR-372 associated oncogenicity and CDDP resistance in SAS cells. (A) 5′sgRNA and 3′sgRNA are designed to delete hsa-miR-372-3p. (B) PCR analysis is used to screen the deletion cell subclones. The dotted line indicates the ~300-bp position on the gel electrophoresis image. Cell subclones exhibiting a band below the dotted line and the absence other bands (marked by triangles) are suspected to have a homozygous deletion. (C) qRT-PCR analysis. This reveals almost complete absence of miR-372 expression in the sublcones selected in (B). (D) Western blot analysis revealing the upregulation of ZBTB7A, TRAIL-R1, and TRAIL-R2 expression in nearly all subclones except for subclone #34. (E,F) Invasion assay and anchorage-independent colony formation assay, respectively. The assays show the general decrease of these properties in the deleted subclones that are tested. (G) Flow cytometry analysis to detect apoptosis. The CDDP induced apoptosis is higher in deleted subclones relative to the control cells. (H) Cell viability assay. The miR-372 deleted cell subclones exhibit higher sensitivity to CDDP. ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.