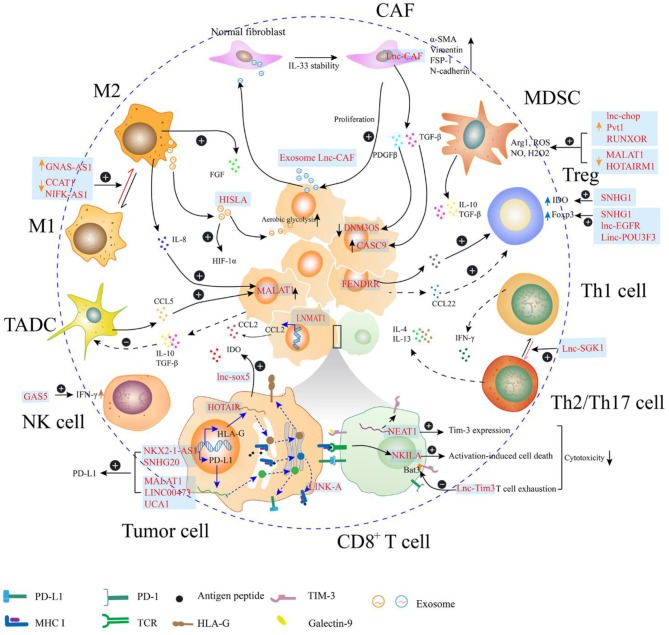
Figure 2.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate the immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment (TME). In the TME, lncRNAs regulate the expression of molecules (e.g., PD-L1, MHC I, and HLA-G) on the surface of the tumor cells, which may attenuate the function of effector T cell. Additionally, the cytotoxicity of T cell can be directly regulated by lncRNAs within T cell, through mediating activation-induced cell death or enhancing T cell exhaustion. LncRNAs can also participate in the phenotype transition of cells, such as helper T cell, fibroblast, and macrophage, which can contribute to the formation of immunosuppressive TME. In the myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC), lncRNAs enhance the production of immunosuppressive molecules, such as Arg1 and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Th1, type 1 helper T cell; Th2, type 2 helper T cell; Th17, T helper cell17; Treg, regulatory T cell; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; CAF, cancer-related fibroblast; M1, M1 macrophage; M2, M2 macrophage; TADC, tumor-associated dendritic cell; NK cell, natural killer cell.