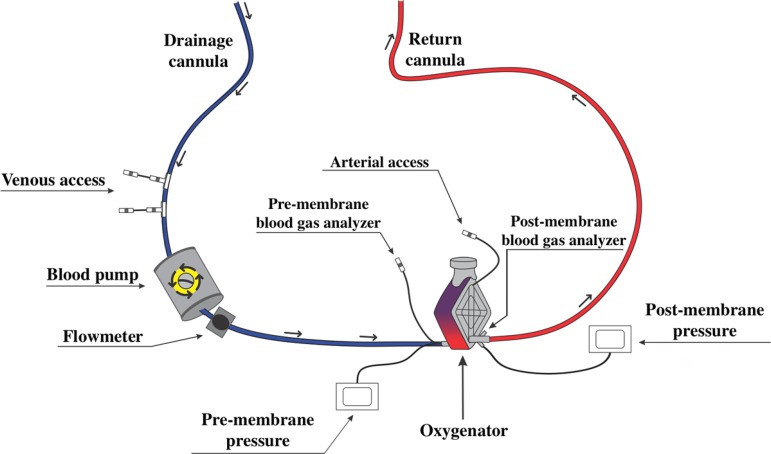
Figure 1.
Diagram of the standard extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit. The venous blood is removed from the patient through a drainage cannula and is pumped (blood pump) to the oxygenator. After passing through the oxygenator, where the oxygenation membrane is, the blood is returned to the patient through an artery (venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) or a vein (venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation). There are access routes located along the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit (venous and arterial access points) for infusion of medications and fluids and collection of laboratory tests, in addition to pressure sensors (pre-membrane and post-membrane) and flow sensors.