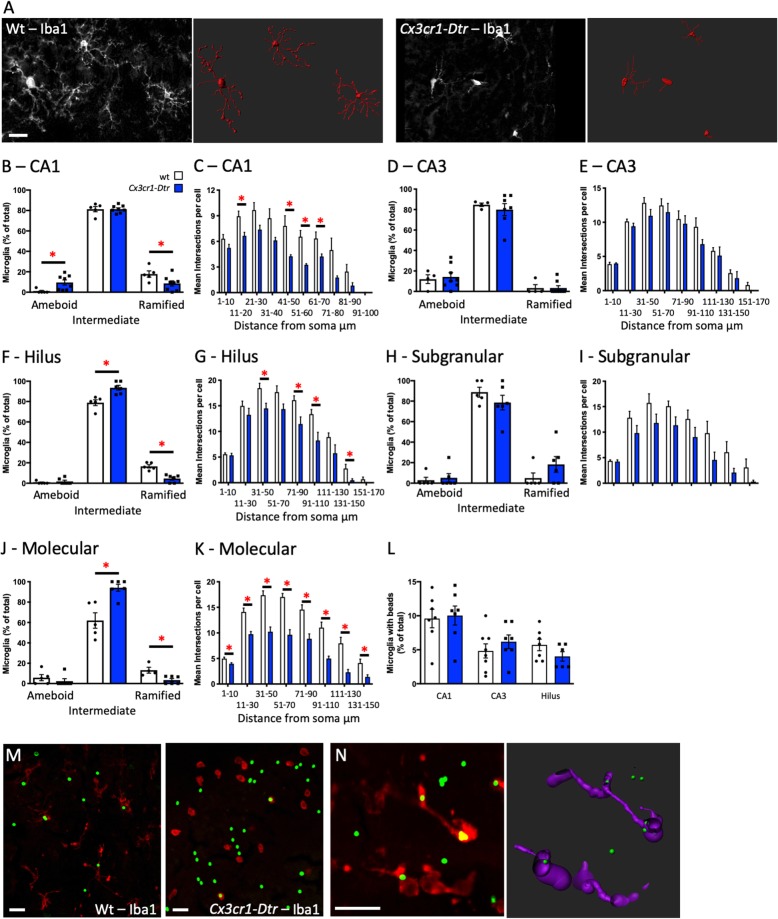
Fig. 6.
Repopulated microglia have a less complex morphology. Microglial profiles at 7 days after diphtheria toxin injection to ablate microglia in Cx3cr1-Dtr rats compared to wild-types (wt). a Representative inverted photomicrographs (white) and reconstructions (red) of microglial profiles generated in Imaris illustrating ramified and ameboid microglia. b Classification of repopulated microglia morphology in the CA1 (increased ameboid 0–1 projections; U = 3, p = 0.0085; n = 5–8). c Assessment of CA1 microglial complexity with Sholl analysis (distance from soma by genotype effect (F(11,66) = 2.76, p = 0.005; n = 5–6). d CA3 classification. e CA3 Sholl analysis. f Hilus classification (increased intermediate 2–4 projections; U = 0, p = 0.0043; fewer ramified 5+ projections; U = 0, p = 0.0043). g Hilus Sholl analysis (distance from soma by genotype effect (F(8, 56) = 4.44, p < 0.001; n = 5). h Subgranular/granular classification. i Subgranular/granular Sholl analysis. j Molecular classification (increased intermediate 2–4 projections; U = 3, p = 0.017; fewer ramified 5+ projections; U = 0, p = 0.0095). k Molecular Sholl analysis (distance from soma by genotype effect (F(7, 49) = 10.17, p < 0.001; n = 5). l Microglial phagocytosis of polystyrene beads in the CA1 region. m Representative photomicrographs of Iba-1-positive cells with phagocytosed microbeads (block arrows). n Example of a microglial cell and its reconstruction showing co-localization of the beads inside the cell. Internalization was verified by imaging the region as a z-stack, transforming the z-stack into a 3D image and visually ensuring that the maximum fluorescence intensity started from within the cell. *p < 0.05; b, d, f, h, j Mann-Whitney U tests; c, e, g, i, k repeated measures ANOVA followed by Student’s unpaired t tests; l Student’s unpaired t tests. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Scale bars A = 50 μm; H = 20 μm; I = 10 μm