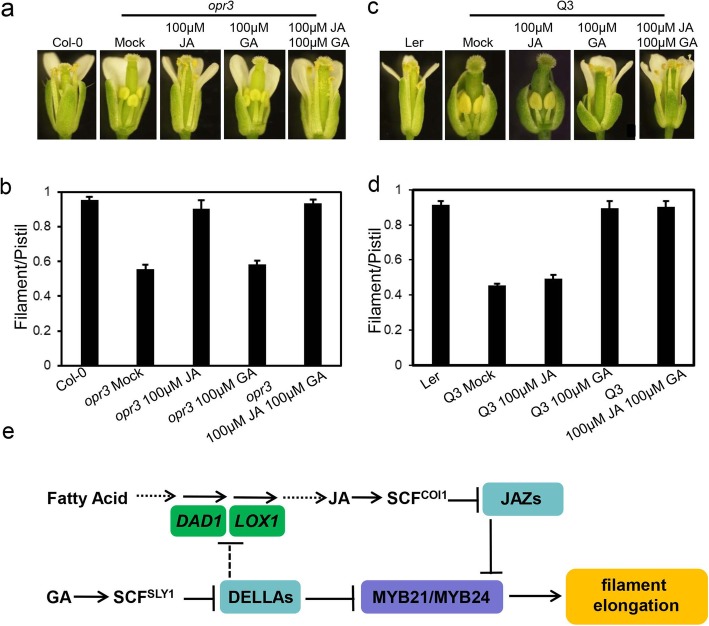
Fig. 3.
DELLAs and JAZs converge on MYB21 and MYB24 to regulate filament elongation. a Comparison of flowers at floral stage 13 in Col-0 and opr3 treated without (Mock) or with methyl jasmonate (JA), gibberellin (GA), or JA plus GA for the indicated concentration. b The ratio of filament length and pistil length at floral stage 13 in the indicated genotypes. Data are means (±SE) of three biological replicates. c Comparison of flowers at floral stage 13 in Landsberg erecta (Ler) wild-type and ga1–3 gai-t6 rga-t2 rgl1–1 (Q3) treated without (Mock) or with methyl jasmonate (JA), gibberellin (GA), or JA plus GA for the indicated concentration. d The ratio of filament length and pistil length at floral stage 13 in the indicated genotypes. Data are means (±SE) of three biological replicates. e A simplified model for the crosstalk between jasmonate and gibberellin in regulating filament elongation. JAZs interact with and inhibit the transcriptional function of MYB21 and MYB24 to suppress filament elongation (Song et al. 2011; Qi et al. 2015). DELLAs inhibit the expression of JA-biosynthesis gene DAD1 and LOX1 (Cheng et al. 2009), and as well as interact with and attenuate MYB21 and MYB24 to inactivate downstream genes and repress filament elongation. JA and GA signal respectively induce degradation of JAZs and DELLAs to derepress MYB21 and MYB24, and synergistically modulate filament elongation in Arabidopsis