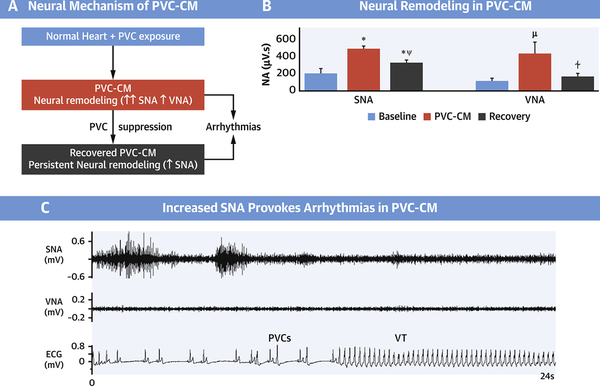
Central Illustration. Neural Remodeling in Premature Ventricular Contraction-Induced Cardiomyopathy.
(A) Proposed Neural Mechanism of Premature Ventricular Contraction-induced Cardiomyopathy (PVC-CM) and consequent pro-arrhythmia. Chronic frequent PVCs cause PVC-CM and neural remodeling. (B) Neural Remodeling in PVC-CM is characterized by increased SNA and VNA. Neural remodeling (increased SNA) persists despite recovery from PVC-CM. (C) In neurally remodeled hearts in PVC-CM and recovered PVC-CM, increased SNA triggers ventricular arrhythmias. ✼ P<0.01 vs Baseline; μ P<0.05 vs Baseline; ⍭ P<0.05 vs PVC-CM; ⍦ P<0.01 vs PVC-CM. Abbreviations: SNA, sympathetic nerve activity; VNA, vagal nerve activity; PVC-CM, premature ventricular contraction-induced cardiomyopathy; VT, ventricular tachycardia.