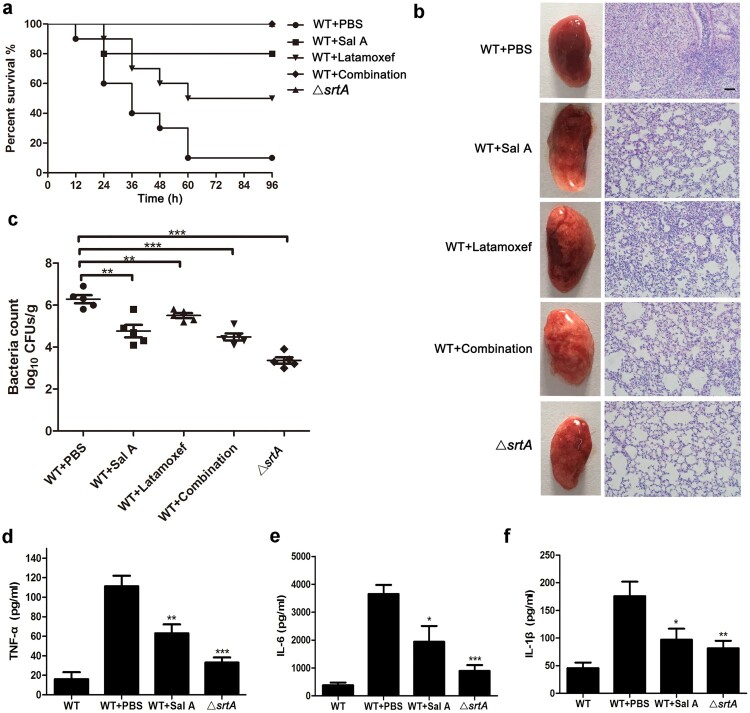
Figure 5.
Sal A protects mice from S. aureus-induced lethal pneumonia. (a) The effect of Sal A on the survival rate in mice challenged with 2 × 109 CFU of S. aureus USA300 or the △srtA strain (10 mice/group) via the i.n. route. The mice were treated with Sal A and/or latamoxef (1 h postinfection, twice a day). The survival of mice was recorded at 12 h intervals for 96 h. (b) Overall pathological changes and histopathological changes in lung tissue from mice treated with or without Sal A. Mice were challenged with 1 × 109 CFU of S. aureus USA300 or the △srtA strain and were treated with or without Sal A and/or latamoxef (1 h post infection, twice a day). At 24 h postinfection, the lungs were removed, and the gross pathological changes and the histopathological changes in the lungs were examined. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) The bacterial load in the lungs 24 h after infection. Mice were challenged with 1 × 109 CFU of S. aureus via the i.n. route and then were treated with or without Sal A and/or latamoxef (1 h postinfection, twice a day). At 24 h postinfection, the lungs were removed, and the bacterial burdens in the lungs were quantified. (d-f) Levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of mice challenged with 1 × 109 CFU of S. aureus USA300. The mice were treated with Sal A or/and latamoxef (1 h postinfection, twice a day). The cytokine levels in BALF were determined 24 h after infection. In each panel, the data shown were collected from three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 using a 2-tailed t test.