Figure 1.
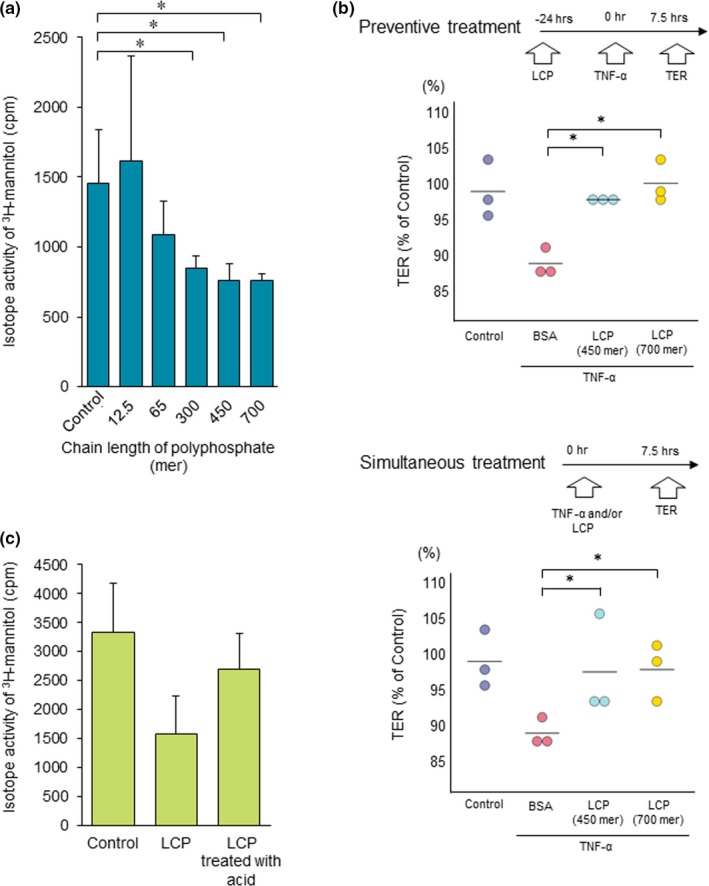
Polyphosphate enhanced the intestinal barrier function in a chain length‐dependent manner. (a) An ex vivo study revealed that the intestinal permeability induced by oxidative stress was significantly attenuated by treatment with 300‐mer, 450‐mer, and 700‐mer polyphosphates (n = 5). (b) The TER test is a method of assessing the resistance between the upper and lower sides of the transwell in vitro. The TER test showed that the permeability induced by TNF‐α treatment was reduced by long‐chain polyphosphate treatment (n = 3). (c) Long‐chain polyphosphates incubated under acidic conditions (pH 1.2) for 2 hours did not enhance the intestinal barrier function in an ex vivo study. *P < 0.05 by Student's t‐test. The error bars show the standard deviation. BSA, bovine serum albumin; LCP, long‐chain polyphosphate; NT, no treatment; TER, transepithelial electrical resistance; TNF‐α, tumor‐necrosis factor alpha. [Colour figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
