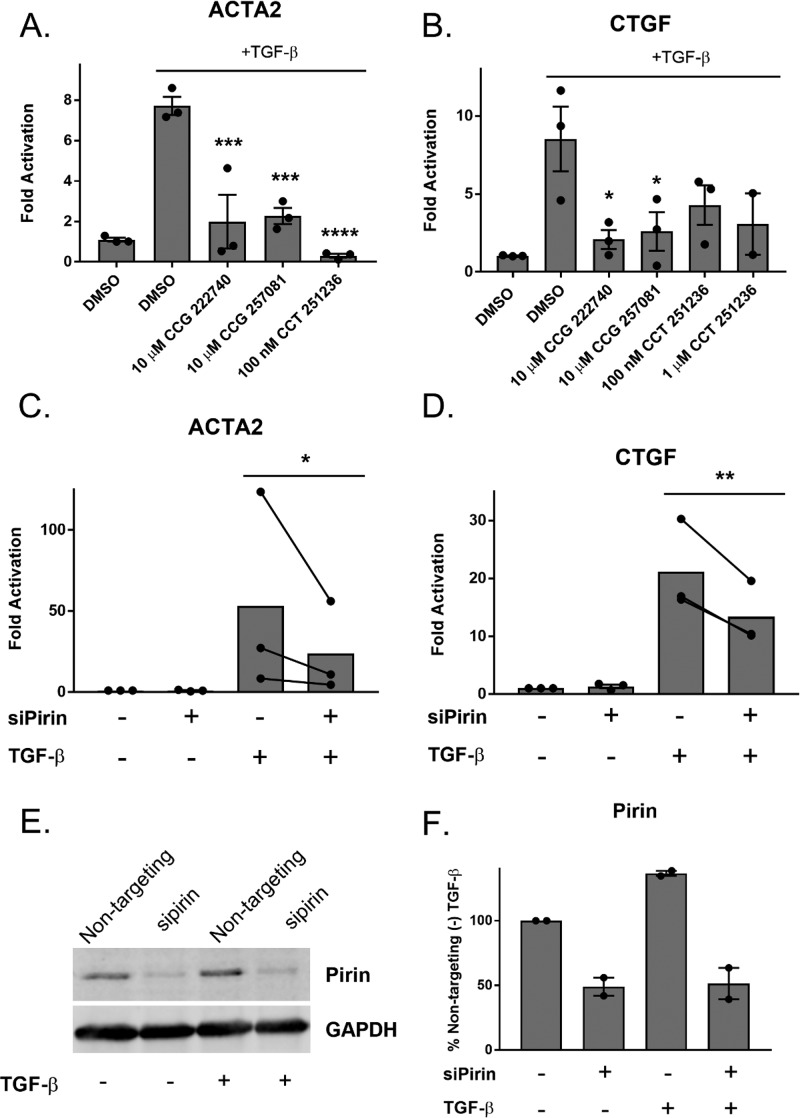
Figure 4.
Inhibition or ablation of pirin reduces TGF-β-dependent gene expression. (A) Primary dermal fibroblasts from healthy donors were treated with TGF-β and either vehicle control, CCG compounds, or CCT251236. Levels of ACTA2 mRNA were measured by qPCR. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM as well as individual mean values. ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test as compared to the (+)TGF-β sample ; n = 3 (B). Similarly, CTGF mRNA levels were measured after treatment with TGF-β and pirin inhibitors. Results are expressed as the overall mean ± SEM *, p < 0.05 using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test as compared to (+) TGF-β; n = 3, except for the 1 μM CCT 251236 condition, which is n = 2. (C) Pirin knockdown reduces TGF-β stimulated ACTA2 mRNA levels in human primary dermal fibroblasts. Results are expressed as the mean as well as individual paired mean values; n = 3. p < 0.05 using a ratio paired t test. Nontargeting siRNA was used in siPirin (−) conditions. (D) Pirin knockdown reduces TGF-β stimulated CTGF mRNA levels. Primary dermal fibroblasts were treated similarly to C. The results are expressed as the overall mean as well as individual paired mean values from three independent experiments (**, p < 0.01). (E) Western blot of pirin protein after siRNA treatment. (F) Quantification of E. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments.