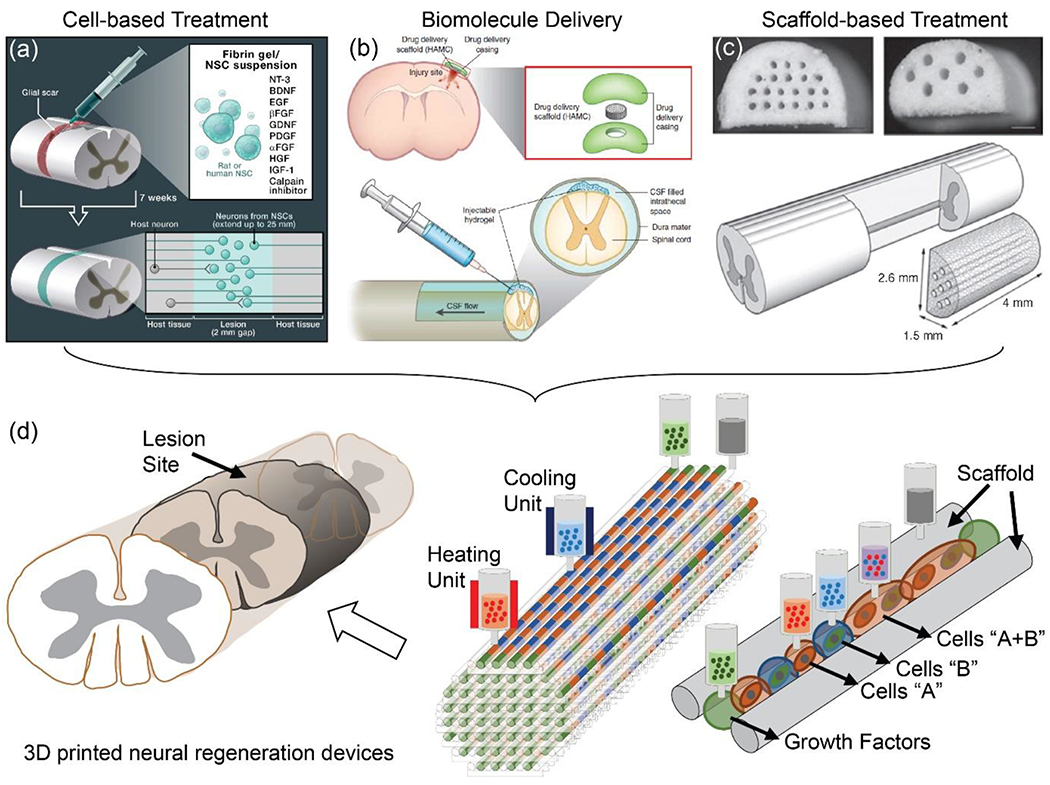
Figure 1.
Strategic design of a 3D printed nervous system scaffold to promote neural regeneration. Neural regeneration refers to the re-establishment and repair of functional neural connections, nervous tissue, and cells by (a) controlling the position, growth, and differentiation of transplanted cells [Reproduced with permission.[8] Copyright 2012, Elsevier.], and (b) promoting neurite networks (e.g., sensory and motor) via the inclusion of biomolecules such as neurotrophic factors [Reproduced with permission.[9] Copyright 2014, Nature Publishing Group], (c) within desired channels in the scaffolds [Reproduced with permission.[10] Copyright 2009, Elsevier.]. (d) 3D printing offers promising combinatorial strategies for neural regeneration, by using a common platform to print scaffolds, cells, and biomolecules. Reproduced with permission.[15] Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.