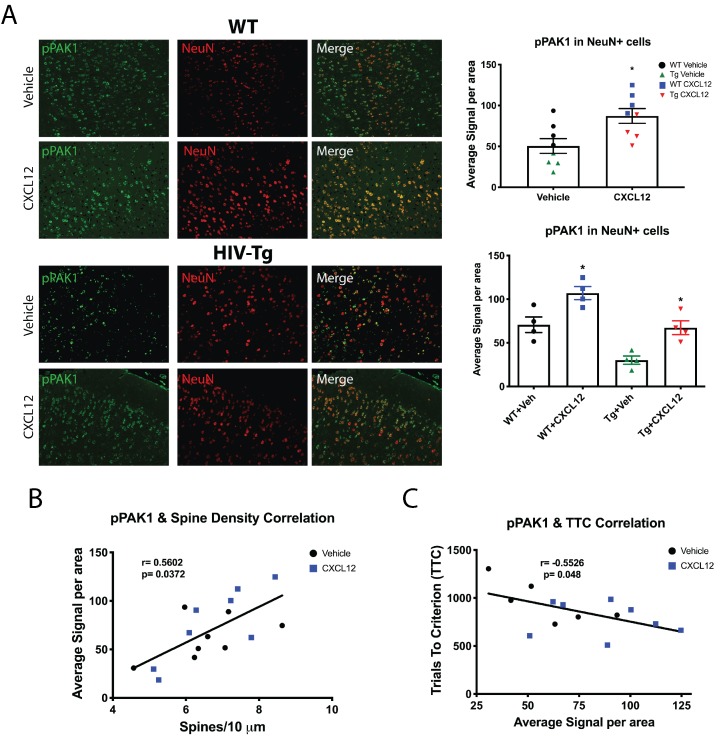
Figure 7. CXCL12 administration increases phosphorylation of PAK1 in layer II/III pyramidal neurons in the mPFC of male WT and HIV-Tg rats.
(A) Sections from the contralateral hemisphere used for dendritic spine analysis were subjected to immunohistochemical and multispectral analysis. Both adult male WT and HIV-Tg rats treated with CXCL12 had a significant increase in pPAK1 levels in NeuN+ cells in the mPFC. N = 4/group, *p<0.05 for WT+Veh vs WT+CXCL12, *p<0.05 for WT+CXCL12 vs Tg+CXCL12, and *p<0.05 for Tg+Veh vs Tg+CXCL12. (B) Phosphorylation of PAK1 in the mPFC was positively associated with overall dendritic spine density in the same set of animals. N = 14 animals, Pearson’s r = 0.5602, p=0.0372. (C) Levels of phosphorylated PAK1 are negatively correlated with the number of trials to criterion on the set shift phase. N = 14 animals, Pearson’s r = −0.5526, p=0.048.