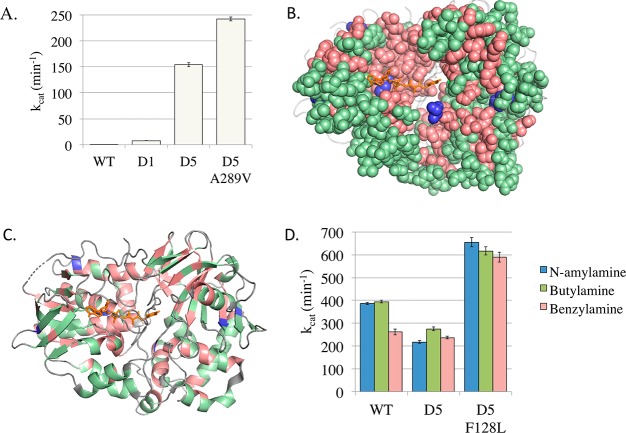
Figure 4.
Enzymatic improvements for selected MAO-N variants. (A) The most significant improved activity to the primary target non-native substrate α-methylbenzylamine was demonstrated by the D5 variant A289V, exhibiting a 1.6-fold increase to that of D5. (B) Every amino acid mutated in this study is shown, with its color denoting whether it (i) showed strong selection for the wild-type amino acid (red); (ii) exhibited robustness, where at least one alternative mutation could be accommodated while still maintaining activity (green); and (iii) exhibited strong selection for a new mutation that increased kcat (blue). (C) Amino acid selection (as in panel B) showing the secondary structure elements. Images generated using PyMol using MAO-N D5 structure (2vvm). (D) Improved activity to three native amine substrates was shown by the D5 variant F128L, with a kcat between 1.6 to 2.25-fold higher than the WT, and 2.2 and 3-fold higher than the parent D5 variant.