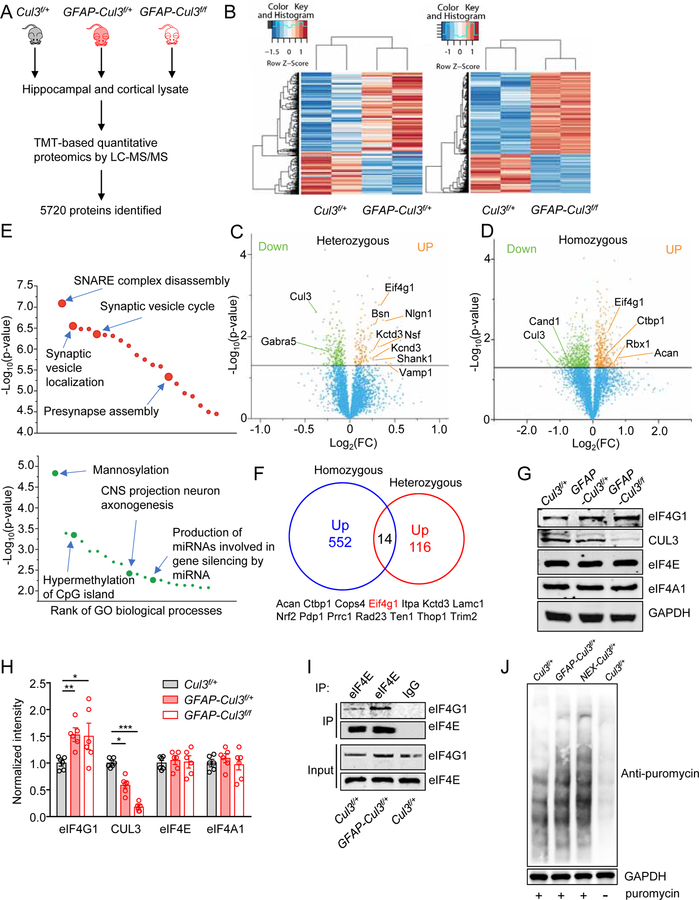
Figure 4. Abnormal expression of synaptic and autism-related proteins in CUL3 deficient brains.
(A) Schematic workflow of quantitative proteomic analysis. Proteomic data were obtained from pooled hippocampus and cortex. n = 3–4 mice for each group (P14, male).
(B) Heat maps of DE proteins in GFAP-Cul3f/+ and GFAP-Cul3f/f brains samples, compared with Cul3f/+ brains.
(C) Volcano plot for DE proteins (116 upregulated, 219 downregulated) in GFAP-Cul3f/+ (heterozygous) brain samples, compared with Cul3f/+ brains. Green and orange dots indicate statistically DE proteins.
(D) Volcano plot for DE proteins (552 upregulated, 914 downregulated) in GFAP-Cul3f/f (homozygous) brain samples, compared with Cul3f/+ brains. Green and orange dots indicate statistically DE proteins.
(E) GO enrichment analysis of DE proteins. DE proteins were enriched in biological processes including ‘SNARE complex disassembly’, ‘Synaptic vesicle localization’, ‘Mannosylation’ and ‘CNS projection neuron axonogenesis’. Full results of the analysis are presented in Supplementary Figures. 8A and 8B.
(F) Proteins upregulated in both GFAP-Cul3f/+ and GFAP-Cul3f/f mice brains.
(G) Representative blots for cortical tissues collected from P14 Cul3f/+ and GFAP-Cul3f/+ and GFAP-Cul3f/f mice.
(H) Quantification analysis of data in (H). Band densities of interested proteins were normalized by the loading control GAPDH; values of control mice were taken as 1; n = 6 mice per each genotype; eIF4G1, Cul3f/+ (1.01 ± 0.15) vs GFAP-Cul3f/+ (1.59 ± 0.14), p = 0.0458; Cul3f/+ vs GFAP-Cul3f/f (1.71 ± 0.3), p = 0.0319; CUL3, Cul3f/+ (1.02 ± 0.11) vs GFAP-Cul3f/+ (0.58 ± 0.07), p = 0.0012, Cul3f/+ vs GFAP-Cul3f/f (0.18 ± 0.03), p < 0.0001; One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.
(I) Increased association of eIF4G1 with eIF4E proteins in GFAP-Cul3f/f mice, compared with Cul3f/+ mice. Hippocampus lysates were incubated with mouse eIF4E antibody and immunoprecipitates were probed for eIF4G1.
(J) Increased Cap-dependent translation in DIV14 GFAP-Cul3f/+ and NEX-Cul3f/+ neurons as measured with SUnSET.
Data were shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, no significant difference.