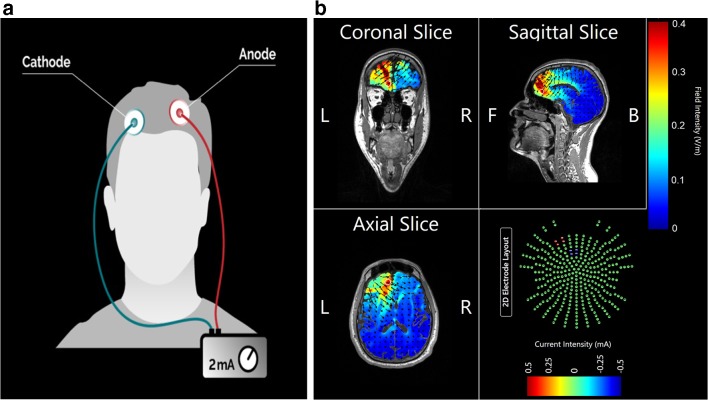
Fig. 2.
a In transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), current (≤2 mA) is generated from a power source and enters the brain through the scalp via the anode; electrical current leaves the brain through the cathode. This results in small shifts in resting membrane potentials that can be harnessed for clinical therapeutic applications in AUD. Image demonstrates a sample electrical field map typically used to model effects of tDCS. b In this example, 2 4-cm sponges have been placed over EEG coordinates AF7 (anode) and Fz (cathode). Scale is electrical field strength in volts per meter; figure created using ROAST [43]