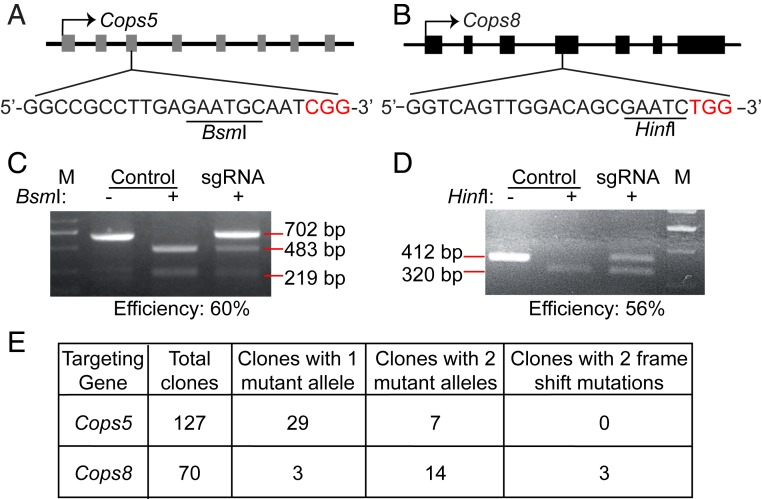
Fig. 1.
Failure in construction of Cops5 KO ESC line by CRISPR/Cas9. (A and B) Schematic illustration of sgRNA design for Cops5 (A) and Cops8 (B). Gray and black rectangles represent the exons of Cops5 and Cops8, respectively. The restriction endonuclease sites in the sgRNA recognition sequences are underlined, and the protospacer-adjacent motifs are shown in red. (C and D) Cutting efficiency of Cas9 at the Cops5 (C) and Cops8 (D) loci. ESCs were transfected with pX330 plasmids targeting Cops5 (C) and Cops8 (D) or with the pX330 plasmid without an sgRNA insert. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were harvested for genomic DNA purification. DNA fragments of 702- and 412-bp around the Cas9 target sites at the Cops5 and Cops8 loci were amplified by PCR, respectively. The DNA fragments were digested by BsmI or HinfI. The intensities of DNA bands were quantified using Image J software, and the cutting efficiency was calculated. (E) Genotypes of ESC clones after Cas9 treatment. ESCs were transfected as described in C and D. Forty-eight hours after transfection, ESCs were treated with trypsin and plated at low density. After 5 to 7 d, individual colonies were picked, expanded, and subjected to genotyping.