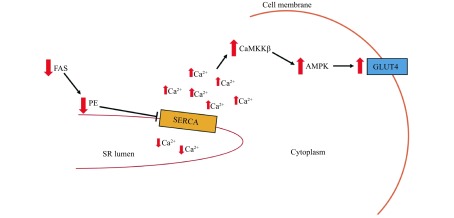
3. Mechanism of enhanced insulin sensitivity in FAS deficient mice.
Suppression of FAS, and thus FAS-facilitated PE synthesis, at the SR results in a reduction of SR PE content. Correspondingly, SERCA activity is impaired leading to decreased Ca2+ uptake into the SR lumen and subsequent accumulation of cytosolic Ca2+. CaMKKβ is activated by cytosolic Ca2+ which leads to increased phosphorylation and therefore, activity of AMPK. AMPK activation induces the translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane and thus, enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and improves skeletal muscle glucose homeostasis. FAS: fatty acid synthase; SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum; PE: phosphatidyl ethanolamine; CaMKKβ: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-β; AMPK: 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase.