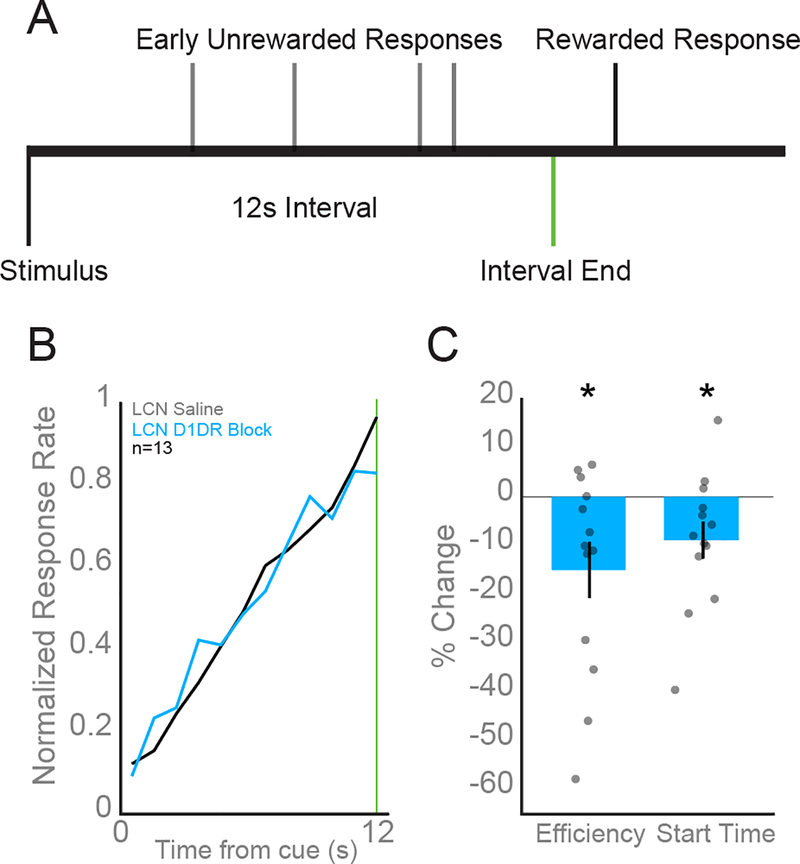
Fig 3: D1DR antagonist SCH23390 in the LCN impairs interval timing performance.
A) Rodents estimated the passage of a 12 s period by making a lever press. The house light turning on served as the stimulus that signaled the start of each trial. Water reward was dispensed for the first lever press that occurred following the elapse of 12 s. B) Average response histograms indicate animals with D1DRs in the LCN blocked using 0.5μl of 1 mg/mL SCH 23390 (blue) responded as if the interval had elapsed earlier compared to responses in saline sessions (black). C) Additionally, animals with LCN D1DRs blocked had significantly impaired interval timing efficiency and response start times compared to control sessions with LCN saline in 12 s trials. All data are presented as mean +/− SEM. Asterisks indicate significance at p<0.05.