Figure 1.
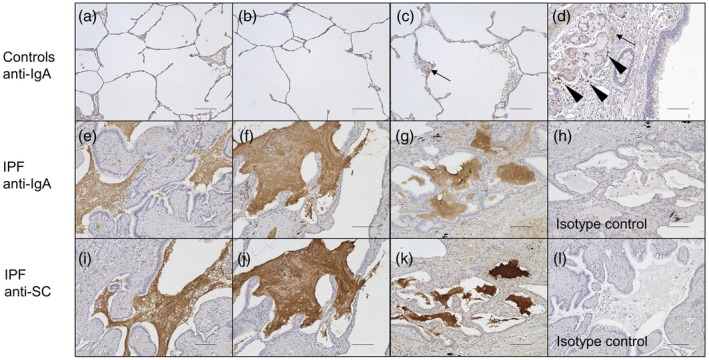
Immunohistochemistry of lung sections of control subjects (n = 3) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients (n = 3). Lung sections were stained with anti‐immunoglobulin (Ig)A antibody (controls, a–d; IPF, e–g) or anti‐SC antibody (IPF, i–k). Representative images from all patients’ lung sections are shown. Accumulated mucus was highly positive for IgA and was adjacent to the epithelia of remodeled tissue in IPF lungs (e–g). These findings were not observed in control lungs (a–c), while bronchial glands, mononuclear cells around bronchial glands (d, arrowhead) and serum in vessels (c,d, arrow) were stained by anti‐IgA antibody. The mucus in IPF lungs was also positive for secretory component (SC) (i–k). Non‐specific staining was not observed with the isotype control antibodies (isotype control for anti‐IgA antibody, h; isotype control for anti‐SC antibody, l). The bars represent 100 µm.
