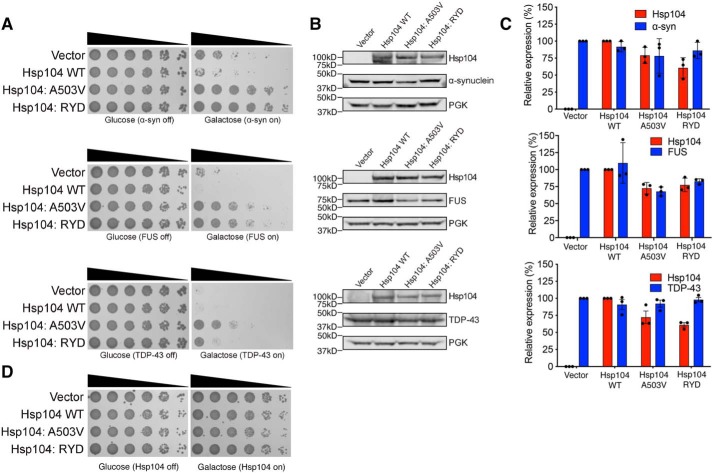
Figure 4.
Hsp104–RYD is a potentiated variant. A, Hsp104–RYD antagonizes α-synuclein, FUS, and TDP-43 toxicity. Empty vector, Hsp104 (WT), Hsp104A503V, or Hsp104–RYD plasmids were transformed into W303aΔhsp104 yeast strains integrated with galactose-inducible α-synuclein-YFP, FUS, or TDP-43. Yeast were serially diluted 5-fold and spotted in duplicate onto galactose (inducing) and glucose (noninducing) media. B, samples were also processed for immunoblotting to assess Hsp104, PGK1 (loading control), and α-synuclein–YFP, FUS, or TDP-43 expression. Molecular mass markers are indicated (left). C, quantification of immunoblots from B. Hsp104 levels (red bars) were normalized to PGK (loading control), and the relative expression level compared with Hsp104 WT was determined. α-Synuclein–YFP, FUS, and TDP-43 levels (blue bars) were normalized to PGK (loading control), and the relative expression level compared with vector control was determined. Data are displayed as scatterplot with bar representing mean ± S.D. (n = 3). D, Hsp104–RYD is not toxic to yeast at 30 °C. Empty vectors, Hsp104 (WT), Hsp104A503V, or Hsp104–RYD plasmid were transformed into W303aΔhsp104 yeast strains. Yeast were serially diluted 5-fold and spotted in duplicate onto galactose (inducing) and glucose (noninducing) media.