FIGURE 1.
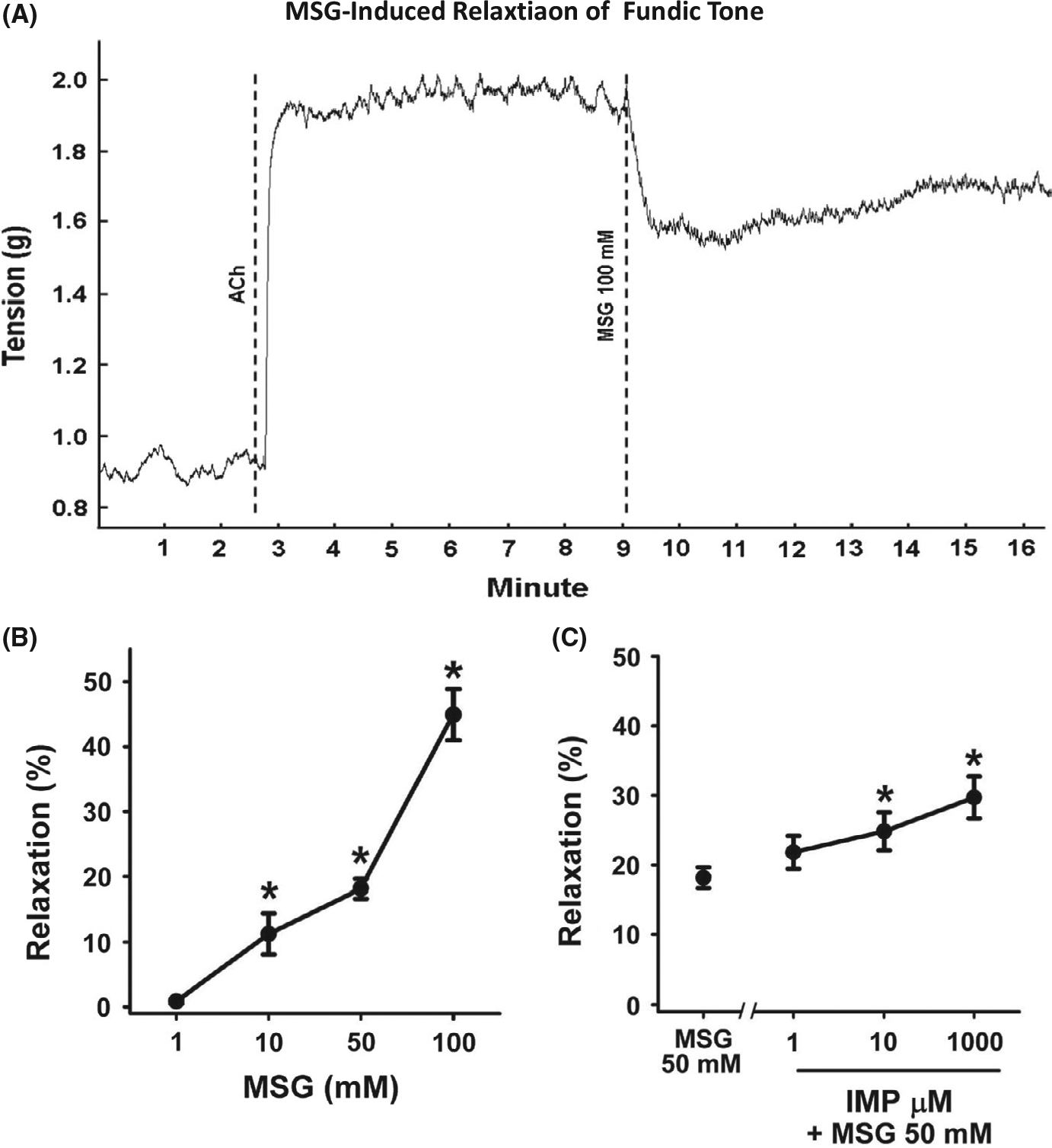
Inhibition of tonic muscle contraction by MSG and MSG plus IMP in muscle strips from fundus. A, Representative tracing illustrating the contraction of the muscle strip from fundus in response to acetylcholine (ACh, 100 μmol/L) and inhibition of contraction by MSG (100 mmol/L). The average increase in tension in response to ACh is 0.8 g. Dotted lines indicate the time at which the agents were added. B, Concentration-dependent relaxation by MSG. Relaxation was calculated as percent inhibition of ACh (100 μmol/L)-induced contraction. Data are mean ± SEM, *P < .05, (n = 12–27). C, Concentration-dependent augmentation of MSG (50 mmol/L)-induced relaxation by IMP. Data are mean ± SEM, *P < .05 vs MSG (50 mmol/L), (n = 12–27)
