Figure 8.
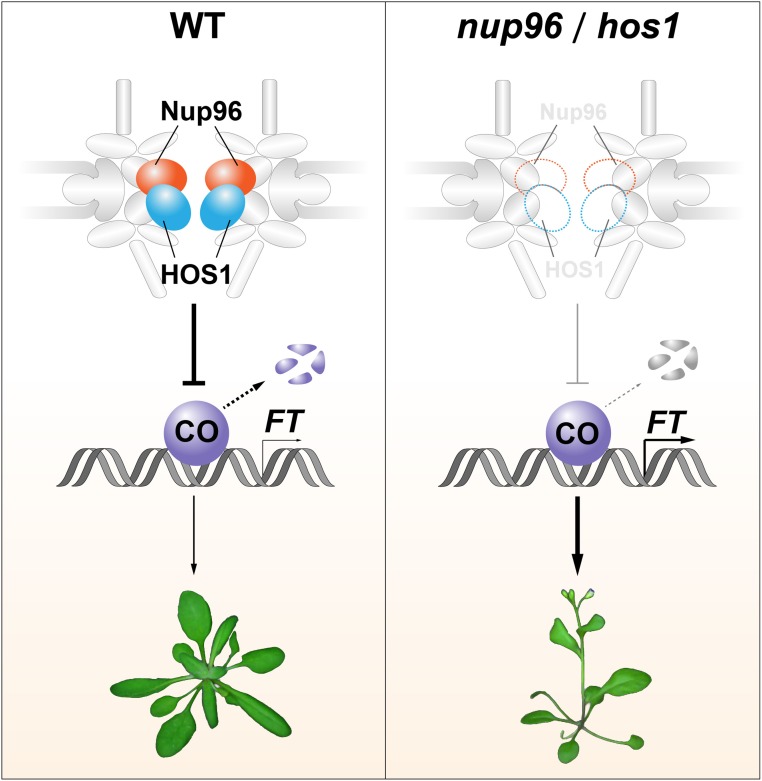
Model Depicting the Molecular Mechanism of Nup96/HOS1-Mediated Flowering Regulation.
In the wild type (left), Nup96 mutually associates with and stabilizes the floral repressor HOS1 to facilitate the degradation of CO proteins, preventing precocious flowering. Loss of either Nup96 or HOS1 function (right) results in the destruction of HOS1 or Nup96 proteins, leading to overaccumulation of CO proteins in plants. The elevated CO abundance enhances FT expression, causing early flowering. WT, wild type.