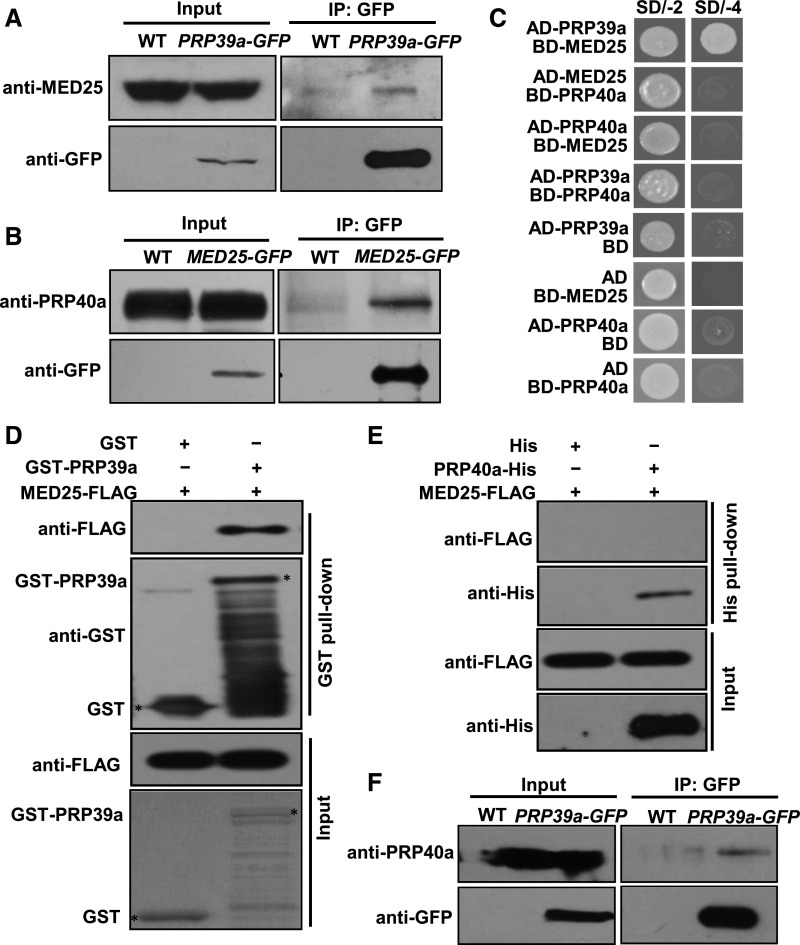
Figure 2.
PRP39a and PRP40a Associate with MED25.
(A) Co-IP assays to verify the interaction of PRP39a and MED25 in vivo. Protein extracts from 10-d–old wild type and PRP39a-GFP seedlings were immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody-bound agarose beads. Total and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.
(B) Co-IP assays to verify the interaction of PRP40a and MED25 in vivo. Protein extracts from 10-d–old wild type and MED25-GFP seedlings were immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody-bound agarose beads. Total and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
(C) Y2H assays to verify the interaction of PRP39a, PRP40a, and MED25 in yeast. Transformed yeast strains with the indicated combinations of constructs were plated on SD medium lacking Leu and Trp (SD/-2) or lacking His, Ade, Leu, and Trp (SD/-4).
(D) In vitro pull-down assay to test the interaction of PRP39a and MED25. A certain amount of MED25-FLAG protein was incubated with recombinant GST-PRP39a fusion protein. Proteins were pulled down by GST Bind Resin, and the eluates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
(E) In vitro pull-down assay to test the interaction of PRP40a and MED25. A certain amount of MED25-FLAG protein was incubated with in vitro-translated PRP40a-His fusion protein. Proteins were pulled down by Ni-NTA His Bind Resin, and the eluates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
(F) Co-IP assays to verify the interaction of PRP39a and PRP40a in vivo. Protein extracts from 10-d–old wild-type and PRP39a-GFP seedlings were immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody-bound agarose beads. Total and immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.