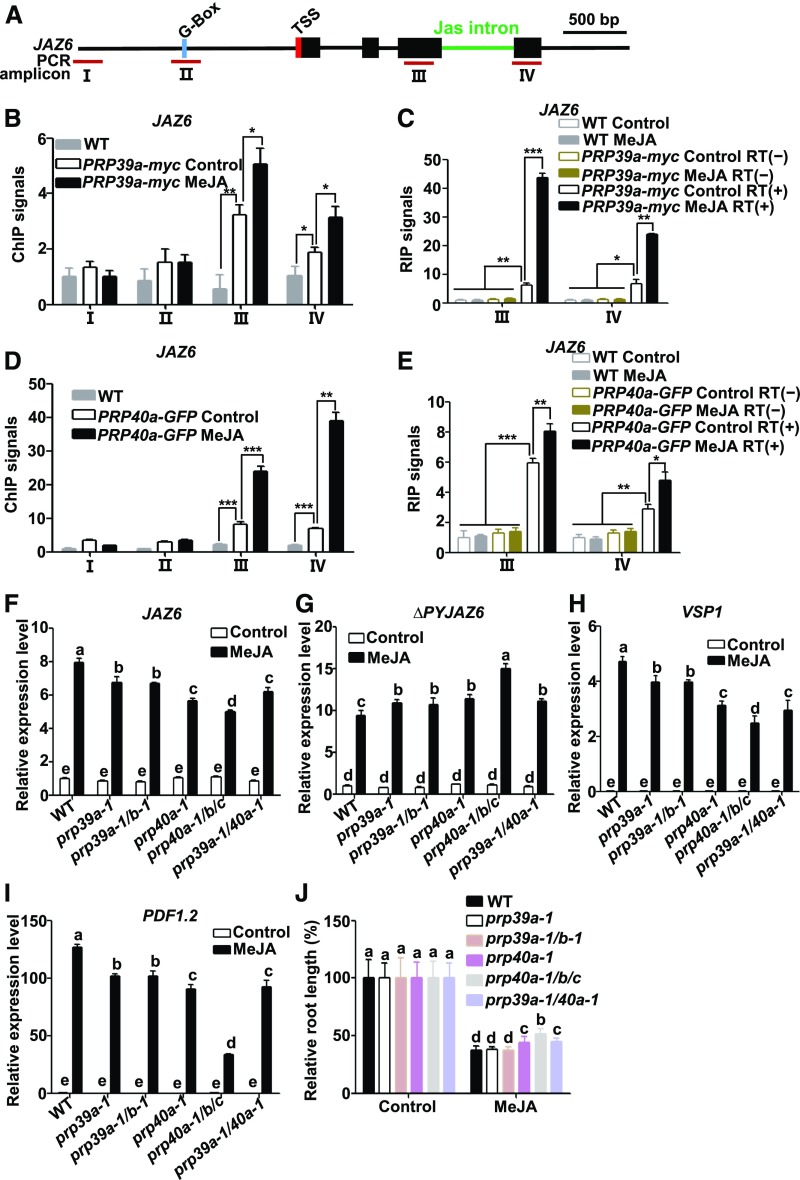
Figure 4.
PRP39a and PRP40a Facilitate the Full Splicing of JAZ6.
(A) Schematic diagrams of JAZ6 and PCR amplicons (indicated as I to IV) used for ChIP-qPCR and RIP-RT-qPCR. Cyan box represents the putative MYC2 binding G-box motif; green line represents the Jas intron; red box represents transcription start site (TSS). Dark-red lines labeled “III” and “IV” represent PCR amplicons used for ChIP-qPCR and RIP-RT-qPCR. Scale bar = 500 bp.
(B) and (D) ChIP-qPCR showing the enrichment of PRP39a (B) and PRP40a (D) on JAZ6 chromatin in response to MeJA. Ten-d–old PRP39a-myc or PRP40a-GFP seedlings were treated without or with 100 μM of MeJA for 30 min before cross linking; wild-type plants without MeJA treatment were used as a negative control. Chromatin from each sample was immunoprecipitated with anti-myc or anti-GFP antibodies. ChIP signals were displayed as the percentage of precipitated DNA relative to input DNA. The value of amplicon I of wild type without MeJA treatment was arbitrarily set to 1. Data shown are mean values of three biological repeats with sd. Asterisks denote significance according to Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. WT, wild type.
(C) and (E) RIP–RT-qPCR showing the enrichment of PRP39a (C) and PRP40a (E) on JAZ6 pre-mRNA in response to MeJA. Ten-d–old PRP39a-myc or PRP40a-GFP seedlings were treated without or with 100 μM of MeJA for 30 min before cross linking; wild-type and precipitated pre-mRNAs without reverse transcription (RT[−]) were used as negative controls. The pre-mRNA from each sample was immunoprecipitated with anti-myc or anti-GFP antibodies. Precipitated pre-mRNA and input pre-mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR for the indicated amplicons. RIP signals were displayed as the percentage of precipitated pre-mRNA relative to input pre-mRNA. The value of amplicon III of wild type without MeJA treatment was arbitrarily set to 1. Results shown are mean values of three biological repeats with sd. Asterisks denote significance according to Student’s t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. WT, wild type.
(F) and (G) RT-qPCR showing JAZ6 (F) and ΔPYJAZ6 (G) expression in response to 100 μM of MeJA in wild type, prp39a-1, prp39a-1/b-1 (prp39a-1/prp39b-1), prp40a-1, prp40a-1/b/c (prp40a-1/prp40b/prp40c), and prp39a-1/40a-1 (prp39a-1/prp40a-1) seedlings. Ten-d–old seedlings were treated without or with MeJA for 30 min before RNA extraction. Expression levels of target genes were normalized to ACTIN7, and the expression levels in wild type without MeJA treatment were arbitrarily set to 1. Data shown are mean values of three biological repeats with sd.
(H) and (I) RT-qPCR showing the MeJA-induced expression of VSP1 (6-h treatment; [H]), PDF1.2 (48-h treatment; [I]) in wild type, prp39a-1, prp39a-1/b-1, prp40a-1, prp40a-1/b/c, and prp39a-1/40a-1 seedlings. Ten-d–old seedlings were treated without or with 100 μM of MeJA for the indicated time points before RNA extraction. Expression levels of target genes were normalized to ACTIN7. Results shown are mean values of three biological repeats with sd. WT, wild type.
(J) Root growth inhibition assay of 8-d–old wild type, prp39a-1, prp39a-1/b-1, prp40a-1, prp40a-1/b/c, and prp39a-1/40a-1 seedlings. Plants were grown on 1/2 MS medium containing 20 μM of JA. The root length of each genotype grown on 1/2 MS medium were arbitrarily set to 1. Results shown are the mean ± sd of measurements from 30 seedlings. WT, wild type.
(F) to (J) Three independent experiments with different seed batches show similar results. Statistical analysis was performed via one-way ANOVA (Supplemental File); bars with different letters are significantly different from each other (P < 0.01).