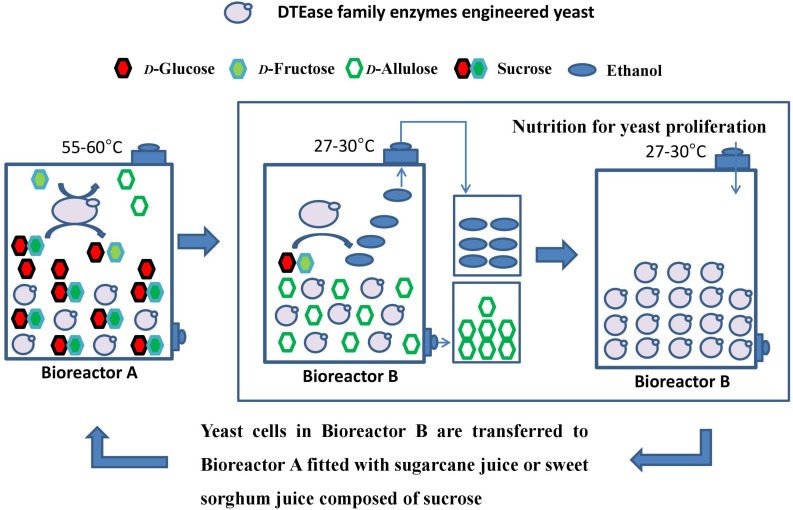
FIGURE 1.
Recycling process for D-allulose conversion and ethanol production by using sugarcane juice or sweet sorghum juice as materials. During catalysis at a high temperature of 55–60°C for 1–2 h in Reaction A, most of the yeast can’t stand such high temperature and die. A small number of yeast spores still survive. These surviving yeast spores proliferate and consume D-fructose and D-glucose to produce ethanol at a later lower temperature of 27–30°C in Reaction B. Besides, a small part of D-fructose was metabolized by the remaining living yeast at such high temperature, but most of D-fructose was still converted into D-allulose in Reaction A.