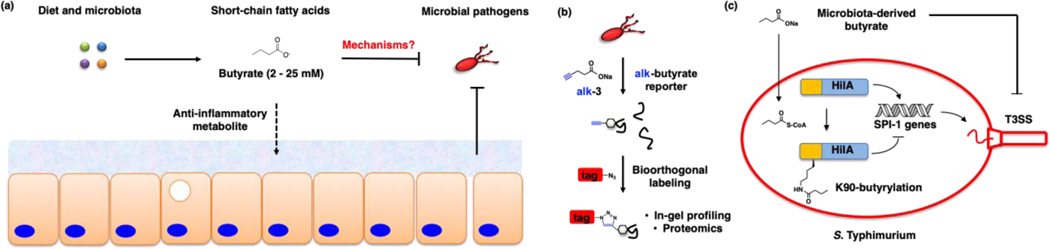
Figure 12.
Microbiota-derived butyrate inhibits enteric pathogen virulence through site-specific protein acylation. (a) Microbiota-derived butyrate is a nutrient source and suppresses host inflammatory pathways as well as inhibits infection by enteric pathogens. (b) Chemical proteomic analysis of butyrate-modified proteins in S. Typhimurium. (c) Site-specific K90-butyrylation of HilA inhibits the expression of S. Typhimurium virulence genes (SPI-1), infection of epithelial cells and mice in vivo (Zhang Z et al, Nat. Chem. Biol., in press).