Figure 57.
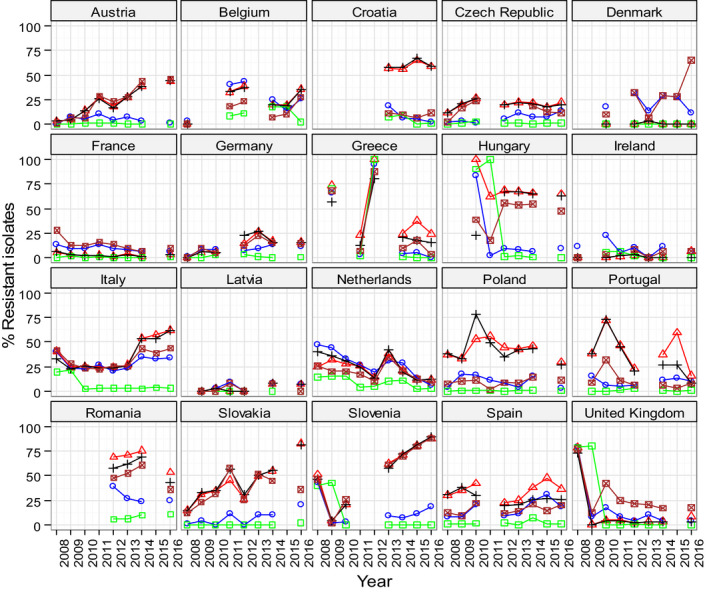
Trends in ampicillin (AMP), cefotaxime (CTX), ciprofloxacin (CIP), nalidixic acid (NAL) and tetracycline (TET) resistance in tested Salmonella spp. from Gallus gallus, EU MSs, 2008–2016
-
Statistical significance of trends over 4‐5 or more years was tested by a logistic regression model (p ≤ 0.05). Statistically significant increasing trends were observed for ampicillin in the Czech Republic, Germany, Italy, Latvia, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia and Spain, for ciprofloxacin in Spain, for ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid in Austria, Germany, Italy, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia, for cefotaxime in Italy, Romania and Slovakia, for nalidixic acid in Hungary, as well as for tetracycline in Austria, Denmark, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Slovenia, Slovakia and Spain.Statistically significant decreasing trends were observed for ampicillin in Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Greece, Hungary, the Netherlands, Poland, Slovenia and the United Kingdom, for ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid in Belgium, Greece, the Netherlands, Poland and the United Kingdom, for cefotaxime in Belgium, Croatia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, the Netherlands, Slovenia, Spain and the United Kingdom, for nalidixic acid in Portugal and Spain, as well as for tetracycline in the Czech Republic, France, Greece, the Netherlands, Portugal, Romania and the United Kingdom.
