Figure 1. Norepinephrine Regulation of CRH Neurons via Local Synaptic Circuits.
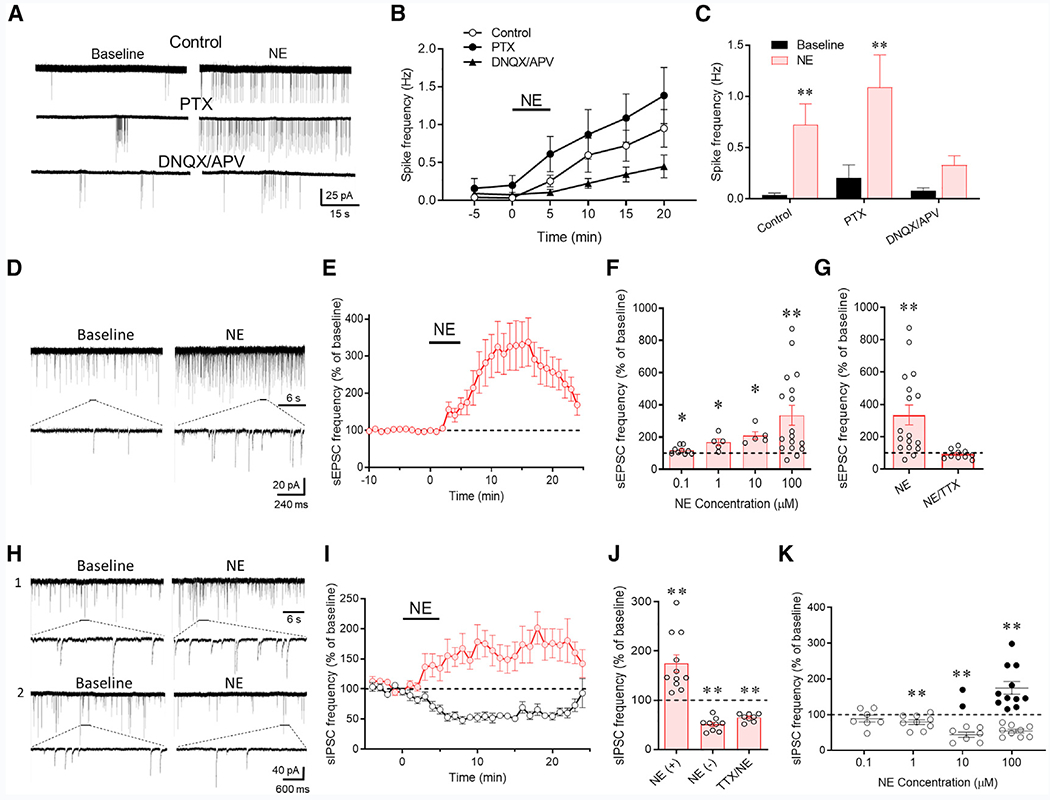
(A) Loose-seal patch clamp recordings of the spiking responses of CRH neurons to bath application of norepinephrine (100 μM) in control aCSF and in GABAA (PTX) and ionotropic glutamate receptor blockers (DNQX/APV).
(B) Time series of changes in spike frequency prior to (−5 to 0 min), during (0–5 min), and after norepinephrine application (100 μM) in control solution, PTX, and DNQX/APV (n = 9–14 cells/group).
(C) Mean spike frequency responses to norepinephrine without (control) and with the GABAA (PTX) and glutamate receptor antagonists (DNQX/APV) (n = 9–14 cells/group).
(D) Whole-cell recording of the effect of norepinephrine (100 μM) on sEPSCs in a CRH neuron recorded in picrotoxin to block sIPSCs.
(E) Time plot of the norepinephrine-induced increase in the frequency of sEPSCs (n = 17 cells).
(F) Concentration dependence of the norepinephrine-induced increase in sEPSC frequency (n = 5–17 cells/group).
(G) The norepinephrine-induced increase in sEPSC frequency was blocked by TTX (n = 10 cells), suggesting action potential dependence.
(H) Whole-cell recording of the norepinephrine (100 μM) effect on sIPSCs in a CRH neuron recorded in DNQX/APV to block sEPSCs. Norepinephrine caused an increase in sIPSCs in some cells (1) and a decrease in sIPSCs in others (2).
(I) Time plots of the normalized increase and decrease in mean sIPSC frequency in response to norepinephrine in different cohorts of CRH neurons (n = 11 and 9 cells, respectively).
(J) Mean norepinephrine-induced increase (NE (+)) and decrease (NE (−) in sIPSC frequency relative to baseline (n = 9 and 8 cells, respectively). The norepinephrine-induced increase, but not decrease, in sIPSC frequency was blocked by TTX (n = 8 cells), suggesting the facilitation (NE (+)), but not the suppression (NE (−)), of sIPSCs by norepinephrine was spike dependent.
(K) Norepinephrine concentration dependence showing that the two sIPSC responses to norepinephrine had different concentration dependencies. The norepinephrine-induced suppression of sIPSCs (open circles) was dominant at lower concentrations, whereas the norepinephrine-induced facilitation of sIPSCs (closed circles) was seen in some but not all recorded cells at higher concentrations (n = 7–9 cells [suppression] and 2–11 cells [facilitation]). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
