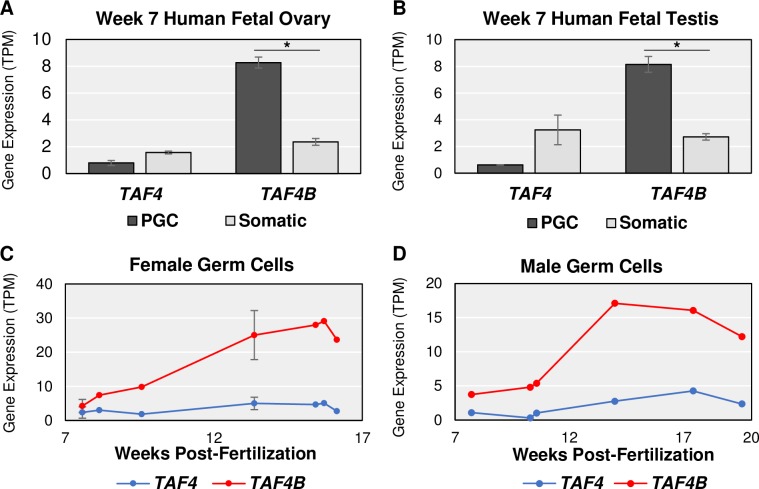
Fig 3. Human embryonic data resembles Taf4a and Taf4b characteristics in mouse.
(A-B) At 7 weeks post-fertilization, female gonadal cells sorted for alkaline phosphatase-positive, CD117-positive germ cells (PGC) and male gonadal cells sorted for cKit-positive, TNAP-positive PGCs have significantly (* = log2FC > |0.25|, p-adj. < 0.05) greater TAF4B mRNA in comparison to the gonadal somatic cells (Somatic) in both females and males. TAF4 mRNA levels are not significantly different in the two cell populations in both sexes, like the mouse. (C-D) Using cKit-positive germ cells to perform FACS, from ~8 weeks post-fertilization to ~16 weeks post-fertilization in females and to ~20 weeks post-fertilization in males, human TAF4B mRNA expression increases more so than TAF4. Also, TAF4B TPMs is greater in the female human germ cells than the male germ cells, making the expression patterns of TAF4B over time very similar between mice and humans. Error bars indicate ± SEM.