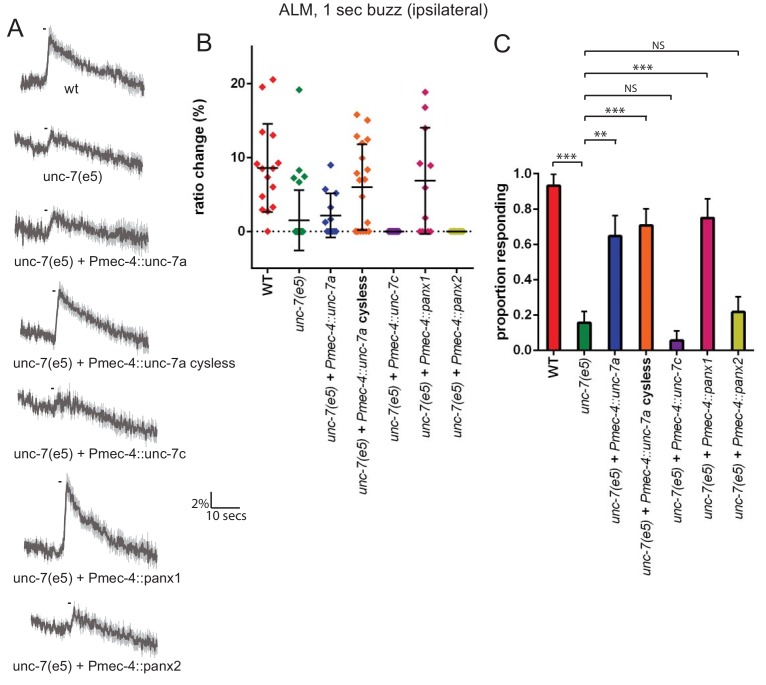
Figure 3. The mechanosensory function of UNC-7 is gap junction-independent.
(A, B, C) Gentle touch responses recorded in ALM for wild type, unc-7(e5), and unc-7(e5) animals expressing unc-7 isoforms or pannexins under the control of Pmec-4. ‘Cysless’ indicates C173A, C191A, C377A, C394A. All neurons recorded were ipsilateral, according to the position of the cell body relative to the stimulation site and the hypothetical midline of the animal. (A) Average traces of % ratio change. Gray indicates SEM. (B) Scatter plot showing individual ratio changes (diamonds). Bars indicate mean ± SEM. (C) Graph showing proportion exhibiting a Ca2+ response. Error bars indicate SE. The response frequency is significantly reduced in unc-7(e5) compared to wildtype (p<0.0001). This is significantly rescued by TRN expression of wild type (p=0.001) or cysless unc-7a (p<0.0001). Cysless unc-7 still significantly rescued the mutant when AVM was ablated (p<0.0001), and there was no significant difference between AVM ablated and unablated cysless unc-7-expressing animals (p=0.4701). While unc-7c (p=0.3991) and mouse panx2 (p=0.7257) did not significantly rescue, panx1 did (p<0.0001), Fisher’s exact test (N = 15, 32, 12, 19, 13, 11, 18, in the order shown in the graphs).
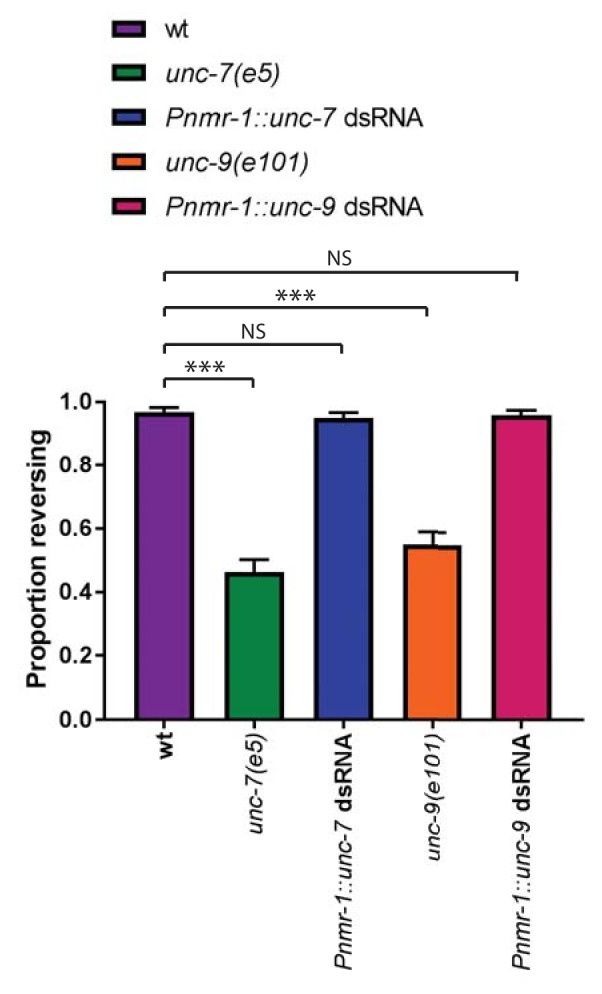
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Expression of unc-7 or unc-9 dsRNA in other neurons does not disrupt the gentle touch response.