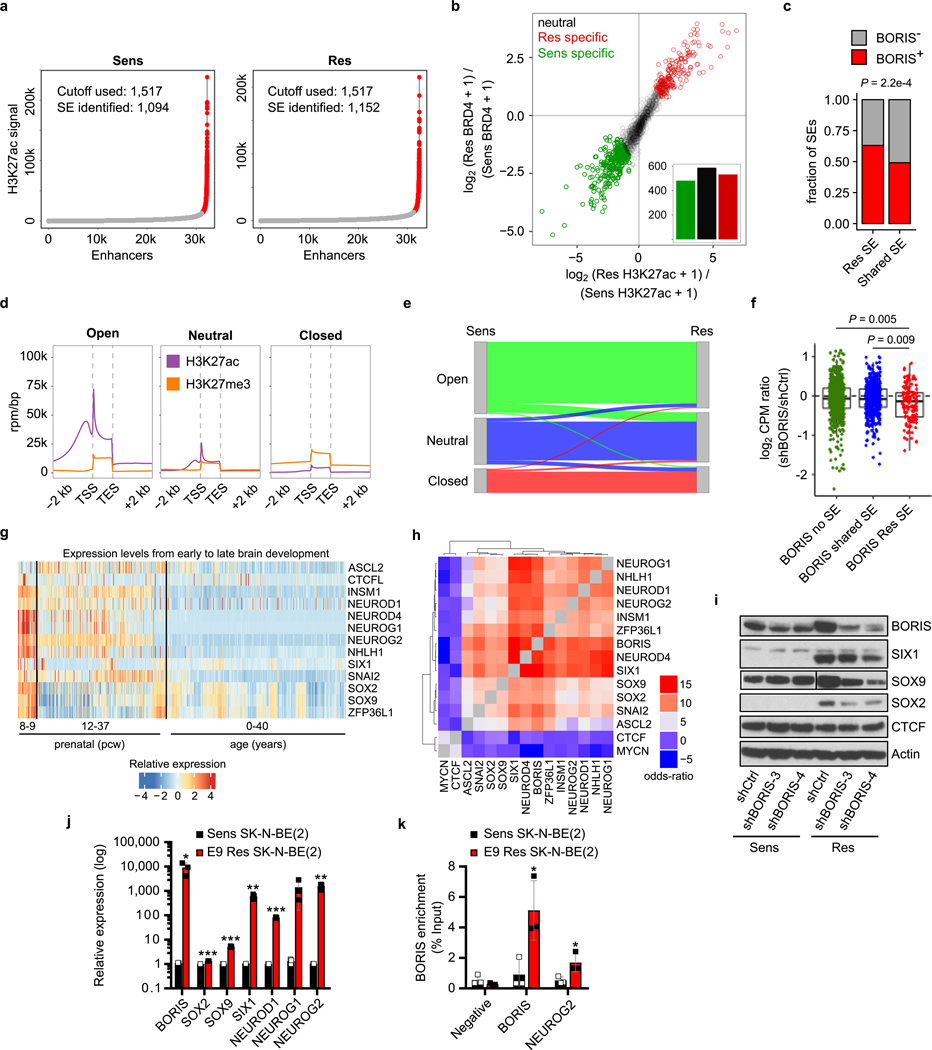
Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Redistribution of the super-enhancer landscape with subsequent expression of a BORIS-dependent proneural network in resistant cells.
a, Accumulation of H3K27ac signal at enhancer regions. Typical enhancers (grey) are plotted according to increasing levels of normalized H3K27ac signal (length × density) in sensitive and resistant cells. The highest cut-off based on the inclination point in both sensitive and resistant cells was used to delineate super-enhancers (red). b, Scatter plot showing differential binding of H3K27ac [log2(RPM per bp + 1)] and BRD4 [log2(RPM per bp + 1)] for all detected super-enhancers in both sensitive and resistant cells. Cell-specific super-enhancers were identified based on the combined increase in H3K27ac and BRD4 binding. For each individual histone mark, a 0.75 log2-transformed fold change threshold was applied and a minimum summed 2.5 log2transformed fold change was used as the final cut-off. c, Bar plot depicting the enrichment (two-sided Fisher’s exact test) and fractions of resistant cell-specific and shared super-enhancers that were located at resistant cell-specific regulatory loop anchors in resistant cells. d, Density plots showing the aggregated accumulation of H3K27ac and H3K27me3 at gene regions, defined as 2 kb upstream of the TSS and 2 kb downstream of the transcription end site (TES). k-means clustering (k = 3) analysis resulted in the separation of genes associated with ‘open’, ‘neutral’ or ‘closed’ chromatin in both sensitive and resistant cells. e, Sankey diagram of the distribution of genes in distinct chromatin states and the switches between sensitive and resistant cells. f, Box plots showing the expression level changes upon BORIS depletion for genes that had a resistant cell-specific and BORIS-positive regulatory interaction and were not associated with a super-enhancer (n = 720), associated with a super-enhancer in both cell types (n = 514) or associated with a super-enhancer seen only in the resistant cells (n = 134) (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test). Box plots are as defined in Fig. 4. g, Heat map of the expression levels of the indicated proneural transcription factor genes during brain development (http://www.brain-map.org/). Gene expression levels are represented as z-scores for different developmental time points (n = 413; pcw, post-conceptional weeks). h, Heat map showing the odds ratios (two-sided Fisher’s exact test) for co-detection of the indicated transcription factors based on the scRNA-seq data in resistant cells (n = 6,379). i, Immunoblot analysis of the indicated proteins in sensitive and resistant cells expressing control (shCtrl) or BORIS (shBORIS-3 and −4) shRNAs. j, k, qRT–PCR analysis of the indicated genes (j) and ChIP–qPCR analysis of BORIS binding at the promoter regions of BORIS and NEUROG2 (k) in sensitive and resistant SK-N-BE(2) neuroblastoma cells. Data are mean ± s.d., n = 3 biological replicates in j and k (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; unpaired two-sided t-tests). All other panels except g and h depict data from n = 2 biological replicates (for gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1).