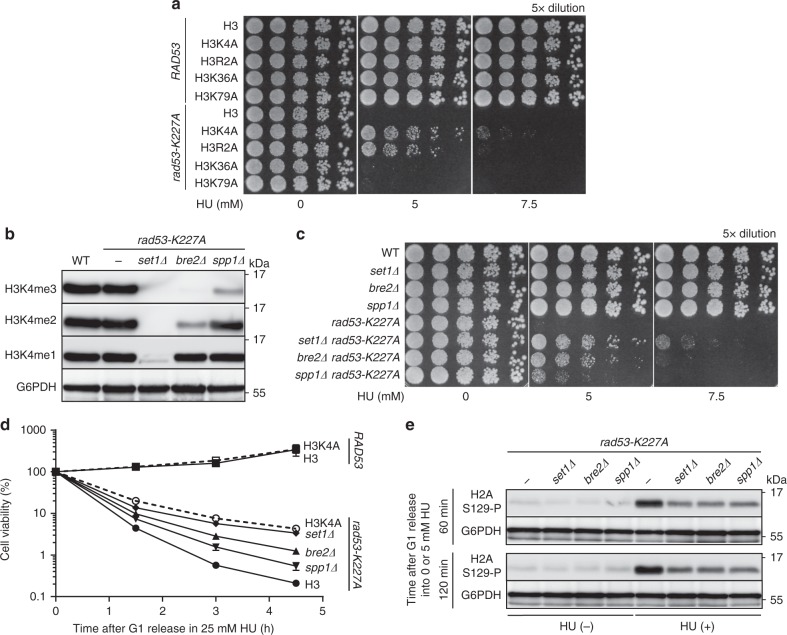
Fig. 1. Decreased H3K4 methylation level improves viability of rad53 mutants exposed to HU-induced replication stress.
a HU sensitivity was determined with H3 (WT), H3K4A, H3R2A, H3K36A and H3K79A mutations in the RAD53 or rad53-K227A backgrounds. b Immunoblot showing H3K4me1/2/3 levels in set1Δ bre2Δ and spp1Δ strains. c HU sensitivity was determined with WT, set1Δ, bre2Δ, and spp1Δ in the RAD53 or rad53-K227A backgrounds. d Cell viability after G1 synchronization and release into 25 mM of HU for the indicated time for H3, H3K4A, set1Δ, bre2Δ and spp1Δ on RAD53 or rad53-K227A backgrounds. Data are the mean ± SD (n = 3 biological replicates). e Immunoblot showing levels of phosphorylated H2AS129 (γH2A) in set1Δ, bre2Δ and spp1Δ on the rad53-K227A background after G1-release in 0 mM (−) or 5 mM HU (+) for the indicated time.