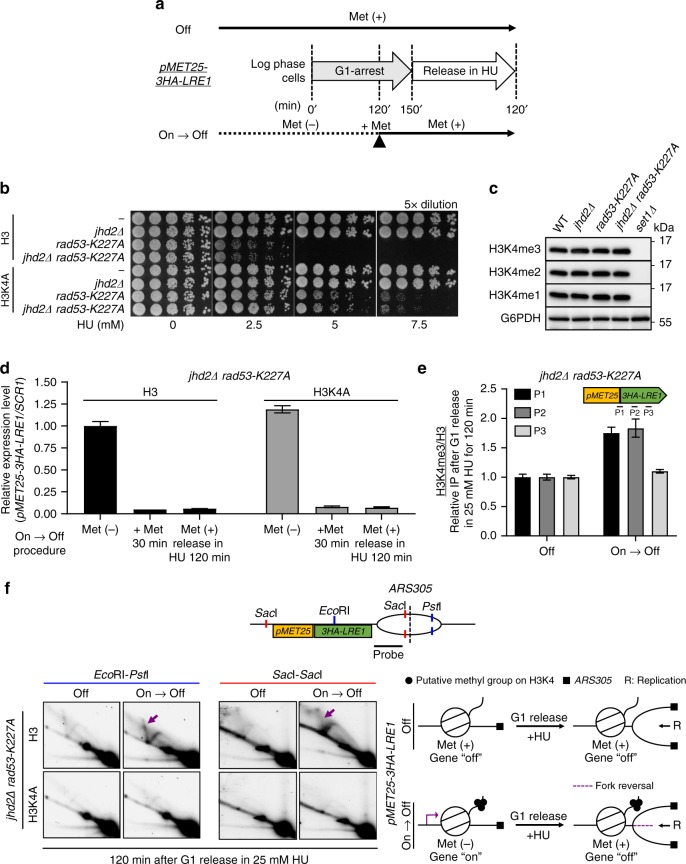
Fig. 5. H3K4 methylation promotes defective replication fork formation in rad53 mutants.
a A schematic representation of the experimental procedure to examine the effect of H3K4me on HU-treated rad53 mutants. b HU sensitivity was determined for JHD2 and jhd2Δ mutants on the RAD53 or rad53-K227A backgrounds with wild-type H3 or H3K4A mutation. c Immunoblot showing H3K4me1/2/3 levels in jhd2Δ strains. d Normalized pMET25-3HA-LRE1 expression in jhd2Δ rad53-K227A with wild-type H3 or H3K4A mutation e H3K4me3 deposition on indicated regions of pMET25-3HA-LRE1 in in jhd2Δ rad53-K227A with wild-type H3 after following the procedure show in a; all error bars represent ± SEM (n = 3 technical replicates). f 2D gel analysis of EcoRI-PstI-digested and SacI-SacI-digested fragments of the ARS305 region in jhd2Δ rad53-K227A with wild-type H3 or H3K4A mutated cells. In brief, cells were G1-released in 25 mM HU with suppressed pMET25-3HA-LRE1 transcription but with low (Off) or high (On → Off) levels of residual H3K4me. The purple arrows indicate spike signals corresponding to aberrant DNA intermediates that accumulated in HU treated rad53-K227A mutant with high level of H3K4me deposition.